shazhongjin
- 2024-10-07
-
发表了主题帖: 【Follow me第二季第2期】智能家庭空气质量监测仪
本帖最后由 shazhongjin 于 2024-11-1 17:56 编辑 **首先感谢 DigiKey得捷 | 电子工程世界EEWorld 举办的Follow me活动,与得捷电子一起解锁开发板的超能力!** ## 前言 大家好,我是沙忠金,一名电子小白。 本期的主板Arduino UNO R4 WiFi,前期几期一直在使用MicroPython 以及 CircuitPython,对于Arduino一直只是门外汉。一直停留在听说过从来未使用过。一直感觉Arduino会很难有抵触情绪在里面。也是借着这次任务学习一下Arduino。 本次任务还有一个很吸引的点就是,可以学习一下开发板如何与HomeAssistant连接以及传输数据。毕竟有再多再好的板子没使用场景、没有想法也是沦为吃灰的玩具。恰好新房子刚刚装修,也是在考虑智能家居的实际应用场景,新房最担心的就是空气质量、甲醛等问题了。那么本次主题为“【Follow me第二季第2期】智能家庭空气质量监测仪” ## 项目介绍 本项目包含以下内容: 入门任务(必做):搭建环境并开启第一步Blink / 串口打印Hello EEWorld! 搭配器件: [Arduino UNO R4 WiFi](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/arduino/ABX00087/20371539) 基础任务(必做):驱动12x8点阵LED;用DAC生成正弦波;用OPAMP放大DAC信号;用ADC采集并且打印数据到串口等其他接口可上传到上位机显示曲线 搭配器件: [Arduino UNO R4 WiFi](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/arduino/ABX00087/20371539) 进阶任务(必做):通过Wi-Fi,利用MQTT协议接入到开源的智能家居平台HA(HomeAssistant) 搭配器件: [Arduino UNO R4 WiFi](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/arduino/ABX00087/20371539) 扩展任务(必做,二选一,或根据自己的兴趣,自定义类似难度或更高难度的任务并完成) ■ **扩展任务一:通过外部LTR-329 环境光传感器,上传光照度到HA,通过HA面板显示数据** 搭配器件: [Arduino UNO R4 WiFi](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/arduino/ABX00087/20371539)、[5591](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/adafruit-industries-llc/5591/16733167)(LTR-329光传感器扩展板)、[PRT-14426](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/sparkfun-electronics/PRT-14426/7652739)(Qwiic缆线-50mm) ■ **扩展任务二:通过外部SHT40温湿度传感器,上传温湿度到HA,通过HA面板显示数据** 搭配器件: [Arduino UNO R4 WiFi](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/arduino/ABX00087/20371539)、[4885](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/adafruit-industries-llc/4885/13694670)(SHT40温湿度传感器扩展板)、[PRT-14426](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/sparkfun-electronics/PRT-14426/7652739)(Qwiic缆线-50mm) 本项目视频及源码: - 视频 [【Follow me第二季第2期】智能家庭空气质量监测仪视频展示](https://training.eeworld.com.cn/video/41250) - 源码 [【Follow me第二季第2期】智能家庭空气质量监测仪代码展示](https://download.eeworld.com.cn/detail/shazhongjin/634545) ## 开箱及展示 购买的配件有: [Arduino UNO R4 WiFi](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/arduino/ABX00087/20371539) [4885](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/adafruit-industries-llc/4885/13694670)(SHT40温湿度传感器扩展板) 开箱全家福: ## 任务成果展示及说明 ### 一、入门任务 搭建环境并开启第一步Blink / 串口打印Hello EEWorld! #### 1. 硬件介绍 本期使用主板是:[Arduino UNO R4 WiFi](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/arduino/ABX00087/20371539) 是一款基于32位Arm® Cortex®-M4 Renesas RA4M1微控制器,具有用于 Wi-Fi® 和蓝牙连接的ESP32模块,具备强大的计算能力和多种连接功能。该板SRAM 32kB,闪存256kB,时钟频率为48MHz,USB端口升级为USB-C,并且最大电源供应电压增加到24V。该板提供了一个CAN总线,允许用户通过连接多个扩展板来最小化布线并执行不同的任务。板载的Qwiic 连接器可以方便地创建即插即用风格的项目。  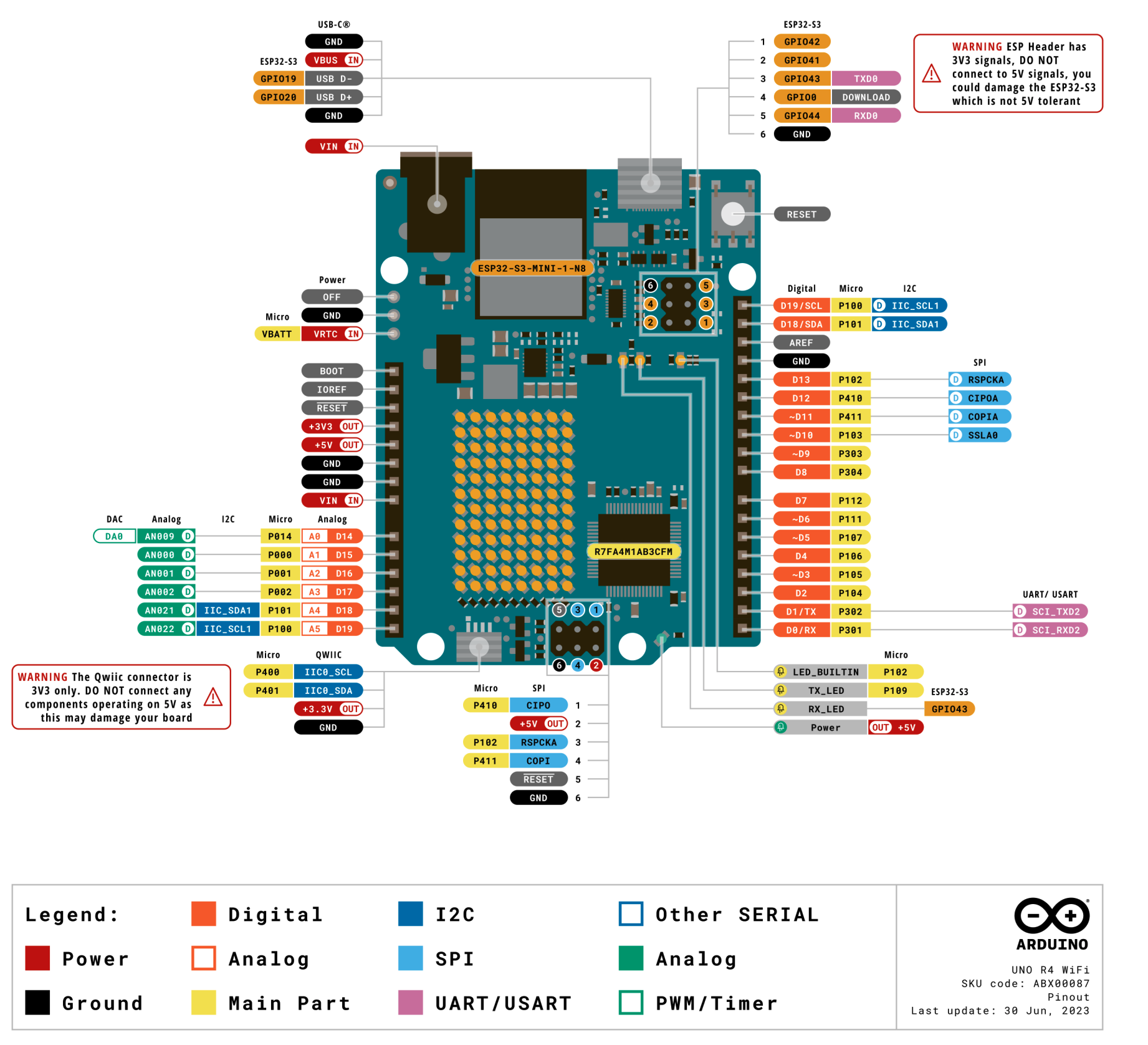 #### 2. 搭建开发环境 1. 访问arduino官网 [https://www.arduino.cc/](https://www.arduino.cc/) ,在官网中点击SOFTWARE进入IDE下载界面。 2. 在Downloads下根据您的操作系统选择适合的安装程序,这里我们选择第一项Windows Win 10 and newer,64bits 3. 找到下载的安装程序“arduino-ide_2.3.2_Windows_64bit”安装后,运行IDE。 4. 点击在左侧开发板管理,也可以通过菜单“工具——开发板——开发板管理”。安装Arduino UNO R4 Boards, 5. 将开发板连接电脑,点击菜单“工具——端口”选择开发板板的端口。可以在连接前后对比多出来的端口就是开发板端口。 6. 点击菜单“工具——开发板”选择Arduino UNO R4 Boards——Arduino UNO R4 WiFi。 7. 随后我们就可以在主界面上来切换不同端口的开发板设备了。 #### 3. Blink / 串口打印Hello EEWorld! 1. 我们同时间隔1s控制板载LED灯开与关,以及向串口输出“Hello EEWorld!”。点击上传等待代码编译及上传后。 2. 点击IDE右上角的“串口监视器”就可以看到开发板向电脑串口输出的消息了。这里还需要注意,开启串口的波特率要与串口监视器的波特率一致才能接收到消息。 #### 4. 软件流程图 #### 5. 代码展示 Follow_me2_task1.ino ``` c++ void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); while (!Serial) delay(10); } void loop() { digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH); delay(1000); digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, LOW); delay(1000); Serial.println("Hello EEWorld!"); } ``` 运行展示 [localvideo]9e5a6e8bb2eb97005b46f5355cf24585[/localvideo] ### 二、基础任务 驱动12x8点阵LED;用DAC生成正弦波;用OPAMP放大DAC信号;用ADC采集并且打印数据到串口等其他接口可上传到上位机显示曲线。 这个任务中有多个任务,我们逐一击破。 #### 1. 驱动12x8点阵LED; **Arduino UNO R4 WiFi** 带有一个内置的 12x8 LED 矩阵,可用于编程以显示图形、动画、充当界面,甚至玩游戏。 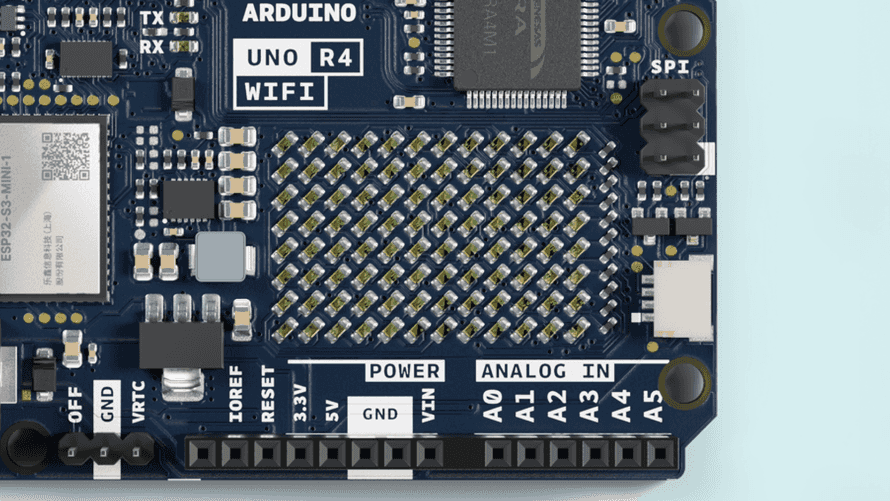 IDE中为我们提供了丰富的示例项目,帮助我们更快的了解每种功能的使用方法。 我们也可以通过官方提供的 LED 矩阵工具[Led Matrix Editor (arduino.cc)](https://ledmatrix-editor.arduino.cc/)来自定义自己的动画。然后点击右上角代码图标,生成下载“animation.h”。 ##### 1. 软件流程图 ##### 2. 代码展示 Follow_me2_task2_1.ino ``` c++ #include "Arduino_LED_Matrix.h" #include ArduinoLEDMatrix matrix; const uint32_t animation[][4] = { { 0xfff801bd, 0xd8018018, 0x31801fff, 66 }, { 0xfff801bd, 0xd8018018, 0x71801fff, 66 }, { 0xfff801bd, 0xd8018818, 0x71801fff, 66 } }; void setup() { Serial.begin(115200); // you can also load frames at runtime, without stopping the refresh matrix.loadSequence(animation); matrix.begin(); // turn on autoscroll to avoid calling next() to show the next frame; the parameter is in milliseconds // matrix.autoscroll(300); matrix.play(true); pinMode(LED_BUILTIN, OUTPUT); } void loop() { digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH); delay(1000); digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, LOW); delay(1000); } ``` ##### 3. 视频展示 [localvideo]f91a2ee6b0d3fe0e316b75dbc3ba1742[/localvideo] --- 更多详细用法参考官方文档:[使用 Arduino UNO R4 WiFi LED 矩阵 |Arduino 文档](https://docs.arduino.cc/tutorials/uno-r4-wifi/led-matrix/) #### 2. 用DAC生成正弦波; **DAC** —— Analog to Digital Converter 用于将数字信号转换为模拟信号。 由于没有示波器,这里使用开发板的DA0接口来采集正弦波。连接示意如下: ##### 1. 软件流程图 ##### 2. 代码展示 Follow_me2_task2_2.ino ``` c++ #include "analogWave.h" // Include the library for analog waveform generation analogWave wave(DAC); // Create an instance of the analogWave class, using the DAC pin int freq = 100; // in hertz, change accordingly void setup() { Serial.begin(115200); // Initialize serial communication at a baud rate of 115200 wave.sine(freq); // Generate a sine wave with the initial frequency wave.amplitude(0.5); //幅值倍数 } void loop() { Serial.print(analogRead(A5)); delayMicroseconds(100); } ``` 读取的波形展示 ##### 3. 视频展示 [localvideo]5853938174ca279838fb5265ae035094[/localvideo] --- 更多详细用法参考官方文档:[Arduino UNO R4 WiFi Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) | Arduino Documentation](https://docs.arduino.cc/tutorials/uno-r4-wifi/dac/) #### 3. 用OPAMP放大DAC信号; OPAMP —— Operational Amplifier 运算放大器,是一种用途广泛且应用广泛的电子元件,属于模拟集成电路类。它的主要功能是放大电压信号,但它们的用途非常广泛,可用于: - 将输入电压镜像到其输出, - 放大一个小的模拟电压到其输出引脚,UNO R4 的输出电压范围为 0 至 ~4.7 V, - 比较两个输入电压并给出二进制“更高”或“更低”输出, - 集成和区分信号。 连接示意如下: #### 4. 用ADC采集并且打印数据到串口等其他接口可上传到上位机显示曲线。 ##### 1. 软件流程图 ##### 2. 代码展示 Follow_me2_task2_4.ino ``` c++ #include "analogWave.h" // Include the library for analog waveform generation #include analogWave wave(DAC); // Create an instance of the analogWave class, using the DAC pin int freq = 200; // in hertz, change accordingly void setup() { Serial.begin(2000000); // Initialize serial communication at a baud rate of 115200 analogReadResolution(14); wave.sine(freq); // Generate a sine wave with the initial frequency wave.amplitude(0.5);//幅值倍数 OPAMP.begin(OPAMP_SPEED_HIGHSPEED); } void loop() { Serial.print(analogRead(A4)); Serial.print(","); Serial.println(analogRead(A5)); delayMicroseconds(100); } ``` 编译上传代码,在IDE点击“串口绘图仪”查看 ##### 3. 视频展示 [localvideo]23c5d804b62cadfe75a6d1042ffcb81e[/localvideo] ### 三、进阶任务 通过Wi-Fi,利用MQTT协议接入到开源的智能家居平台HA(HomeAssistant) #### 1. 硬件介绍 | 硬件 | 链接、资料 | 图片 | | -------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | | Arduino UNO R4 WiFi | [Getting Started with UNO R4 WiFi Arduino Documentation](https://docs.arduino.cc/tutorials/uno-r4-wifi/r4-wifi-getting-started/) | | | Adafruit Sensirion SHT40 Tempera | [Adafruit Sensirion SHT40, SHT41 & SHT45 Temperature & Humidity Sensors Adafruit Learning System](https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-sht40-temperature-humidity-sensor) | | #### 2. 环境配置 ##### 1. HomeAssistant搭建 首先我们先搭建homeassistant环境,这里我使用unraid系统。相较于windows或者是linux上使用命令行会容易许多。 直接在工作台首页中点击“应用”,在应用页面下搜索“homeassistant”。unraid会列出忧患homeassistant的应用。第一个为直接docker拉取镜像的core版的ha,第二个为通过docker安装的虚拟机版的ha也就是os版ha。各个版本差异如下: 这里我就直接安装docker版ha,安装时需要配置下webui的端口号8123默认即可。点击应用后就会自动拉取镜像并且运行。 在浏览器中输入\[IP]\:\[PORT\] 我这里是http://192.168.2.200:8123/,进入homeassistant的webui界面。 ##### 2. MQTT服务器搭建 在工作台首页中点击“应用”,在应用页面下搜索“emqx”。只有一个搜索结果,我们直接安装就好了。 安装后容器自动运行。 在浏览器中输入\[IP]\:\[PORT\] 我这里是http://192.168.2.200:18083/,进入emqx的webui界面。 ##### 3. 配置MQTT 进入homeassistant的webui界面,点击左侧设置标签,在页面中点击设备与服务。 在右下角点击添加集成,在弹出的选择品牌或集成对话框中输入“mqtt”。 然后选择第一个MQTT。 输入MQTT服务器的地址、端口、用户名及密码,这里我的homeassistant与emqx在同一网段内,这里我直接填写内网的IP地址,端口为默认的1883。 连接成功后会提示“成功”,并设置区域。这里直接点击完成即可。 配置完成后,MQTT设备以及实体情况。 #### 3. 软件流程图 1. 初始化: - 设置Wi-Fi和MQTT参数。 - 初始化串口通信。 - 初始化SHT4x传感器。 2. Wi-Fi连接: - 尝试连接到指定的Wi-Fi网络,最多重试5次。 - 连接成功后,输出连接成功的消息。 3. 传感器初始化: - 初始化SHT4x传感器,设置精度和加热器配置。 - 输出传感器初始化完成的消息。 4. MQTT连接: - 连接到MQTT服务器。 - 设置设备名称、软件版本和传感器图标等。 5. 主循环: - 每隔5秒读取温湿度传感器数据。 - 将读取到的数据通过MQTT发送到Home Assistant。 - 处理按钮命令,控制板载LED的开关状态。 #### 4. 代码展示 Follow_me2_task3.ino ``` c++ #include "WiFiS3.h" #include "SPI.h" #include "Adafruit_SHT4x.h" #include "ArduinoHA.h" #include "arduino_secrets.h" #include "arduino_mqtt.h" char sta_ssid[] = SECRET_STA_SSID; // your network SSID (name) char sta_pass[] = SECRET_STA_PASS; // your network password (use for WPA, or use as key for WEP) char addr[] = MQTT_BROKER_ADDR; int port = MQTT_BROKER_PORT; char username[] = MQTT_BROKER_USERNAME; char password[] = MQTT_BROKER_PASSWORD; int status = WL_IDLE_STATUS; // Sensor read intervals (in milliseconds) const unsigned long sensorCInterval = 5000; // other Sensor read intervals 5s const unsigned long reconnectInterval = 600000; // Last time the sensors were read unsigned long previousMillisC = 0; unsigned long previousMillisReconnect = 0; WiFiClient client; // Arduino Home Assistant integration HADevice device("arduino"); //HADevice device(mac, sizeof(mac)); HAMqtt mqtt(client, device); Adafruit_SHT4x sht4 = Adafruit_SHT4x(); HASensor sht4_temperature_sensor("sht4_temperature_sensor"); HASensor sht4_relative_humidity_sensor("sht4_relative_humidity_sensor"); HAButton board_led("board_led"); void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); while (!Serial) delay(10); Adafruit_SHT4x_Init(); reconnect(); device.setName("arduino uno r4 wifi"); device.setSoftwareVersion("1.0.0"); sht4_temperature_sensor.setIcon("mdi:home"); sht4_temperature_sensor.setName("Temperature"); sht4_temperature_sensor.setUnitOfMeasurement("°C"); sht4_relative_humidity_sensor.setIcon("mdi:home"); sht4_relative_humidity_sensor.setName("Humidity"); sht4_relative_humidity_sensor.setUnitOfMeasurement("%"); board_led.setIcon("mdi:fire"); board_led.setName("Click me A"); board_led.onCommand(onButtonCommand); mqtt.setKeepAlive(60); mqtt.begin(addr,port,username,password); } void loop() { unsigned long currentMillis = millis(); mqtt.loop(); char tempbuffer[10]; char humibuffer[10]; // 非阻塞读取sht40传感器数据 5s if (currentMillis - previousMillisC >= sensorCInterval) { previousMillisC = currentMillis; // 获取温湿度传感器sht40数据 sensors_event_t humi, temp; sht4.getEvent(&humi, &temp); Serial.print("Temperature: "); Serial.print(temp.temperature); Serial.println("℃"); Serial.print("Humidity: "); Serial.print(humi.relative_humidity); Serial.println("% rH"); dtostrf(temp.temperature, 6, 2, tempbuffer); dtostrf(humi.relative_humidity, 6, 2, humibuffer); sht4_temperature_sensor.setValue(tempbuffer); sht4_relative_humidity_sensor.setValue(humibuffer); } } void onButtonCommand(HAButton* sender) { if (sender == &board_led) { if (digitalRead(LED_BUILTIN) == HIGH){ digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, LOW); Serial.println("LED light off"); } else{ digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH); Serial.println("LED light on"); } } } void reconnect() { Serial.print("Attempting to connect to SSID: "); Serial.print(sta_ssid); int i = 0; while (status != WL_CONNECTED) { Serial.print("."); status = WiFi.begin(sta_ssid, sta_pass); i++; if (status == WL_CONNECTED){ Serial.println("Connected to WiFi successfully"); //Serial.println(WiFi.localIP()); break; } if(i == 5) break; delay(5000); } } void Adafruit_SHT4x_Init() { Serial.println("Adafruit SHT4x Initializing..."); if (!sht4.begin(&Wire1)) { Serial.println("Couldn't find SHT4x"); while (1) delay(1); } Serial.println("Found SHT4x sensor"); Serial.print("Serial number 0x"); Serial.println(sht4.readSerial(), HEX); // You can have 3 different precisions, higher precision takes longer sht4.setPrecision(SHT4X_HIGH_PRECISION); switch (sht4.getPrecision()) { case SHT4X_HIGH_PRECISION: Serial.println("High precision"); break; case SHT4X_MED_PRECISION: Serial.println("Med precision"); break; case SHT4X_LOW_PRECISION: Serial.println("Low precision"); break; } // You can have 6 different heater settings // higher heat and longer times uses more power // and reads will take longer too! sht4.setHeater(SHT4X_NO_HEATER); switch (sht4.getHeater()) { case SHT4X_NO_HEATER: Serial.println("No heater"); break; case SHT4X_HIGH_HEATER_1S: Serial.println("High heat for 1 second"); break; case SHT4X_HIGH_HEATER_100MS: Serial.println("High heat for 0.1 second"); break; case SHT4X_MED_HEATER_1S: Serial.println("Medium heat for 1 second"); break; case SHT4X_MED_HEATER_100MS: Serial.println("Medium heat for 0.1 second"); break; case SHT4X_LOW_HEATER_1S: Serial.println("Low heat for 1 second"); break; case SHT4X_LOW_HEATER_100MS: Serial.println("Low heat for 0.1 second"); break; } Serial.println("Adafruit SHT4x Initialization Completed"); } ``` arduino_mqtt.h ``` c++ // MQTT服务链接 #define MQTT_BROKER_ADDR "emqx.inversedesign.net" // 这里输入你的mqtt服务器地址 #define MQTT_BROKER_PORT 1883 #define MQTT_BROKER_USERNAME "arduino uno r4 wifi" #define MQTT_BROKER_PASSWORD "arduino uno r4 wifi" ``` arduino_secrets.h ``` c++ // 双引号中输入你的 WIFI 账号密码 #define SECRET_STA_SSID "" #define SECRET_STA_PASS "" ``` #### 5. 视频演示 [localvideo]378f3ed02ebee24b3df64150ff8b19e3[/localvideo] ### 四、扩展任务 #### 1. 硬件介绍 | 硬件 | 链接、资料 | 图片 | | -------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | | Arduino UNO R4 WiFi | [Getting Started with UNO R4 WiFi Arduino Documentation](https://docs.arduino.cc/tutorials/uno-r4-wifi/r4-wifi-getting-started/) | | | Adafruit Sensirion SHT40 Tempera | [Overview Adafruit Sensirion SHT40, SHT41 & SHT45 Temperature & Humidity Sensors Adafruit Learning System](https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-sht40-temperature-humidity-sensor) | | | 攀藤PMS7003——颗粒物传感器 | [PMS7003---激光颗粒物传感器-南昌攀藤科技有限公司 (plantower.com)](https://www.plantower.com/products_16/8.html) | | | 盛思锐SCD41——co2传感器 | [SCD41-突破CO₂ 传感器尺寸壁垒 (sensirion.com)](https://sensirion.com/cn/products/product-catalog/SCD41) | | | DART WZ-H3-NK——HCHO传感器 | [WZ-H3-N型长寿命抗干扰甲醛检测模组-智能传感器模组-深圳市普晟传感技术有限公司-普晟传感-甲醛传感器-一氧化碳传感器-氢气传感器-普晟传感-氢气传感器-氨气传感器-硫化氢传感器-气体传感器-传感器公司 (szprosense.com)](https://www.szprosense.com/?list_28/79.html) | | | ENS160 | [ENS16x Digital Metal-Oxide Multi-Gas Sensor Family - ScioSense](https://www.sciosense.com/ens16x-digital-metal-oxide-multi-gas-sensor-family/) | | #### 2. 硬件连接 Adafruit Sht40 通过Qwiic线缆连接到Qwiic I2C插槽,SCD41 与 ENS160 与板载I2C引脚连接。查看Arduino UNO R4 WiFi开发板的原理图I2C的引脚没有没有连接上拉电阻,SCL与SDA分别与3.3v连接一个10kΩ的电阻。ENS160我购买的是已经焊接好的模块,需要一个3.3v和一个1.8v的供电,3.3v供电开发板上直接就可以获得但是1.8v没有直接来源,需要从5v或3.3v降到1.8v才行。经过查询资料以及淘宝,最终选择了AMS1117-1.8。 WZ-H3-NK的TX、RX与A2、A3连接使用软串口SoftwareSerial读取数据,PMS7003与A0、A1硬件串口连接。连接原型如下 元器件与开发板连接关系以及示例程序调试已经逐一调通,下面我们来为这些元器件设计个PCB。这是我第一次绘制PCB,在立创开源平台上找一些开源项目再配合搭配的元器件的基本电路,终于设计出自己的第一个PCB。在漫长的打样等待中。 经过了前几期的活动的不断学习尝试,焊接技术也有了十足的进步。焊接排针、排母这些连接器不需要事先找找感觉了。贴片元器件也是在几次尝试后成功的焊接上,并测试没有短路断路。 合体后的样子 #### 3. 必要环境搭建 mqtt服务器、homeassistant系统可参考、沿用进阶任务的环境。 #### 4. 软件流程图 1. 初始化: - 设置Wi-Fi和MQTT Broker的参数。 - 初始化各个传感器对象。 - 设置传感器读取间隔时间。 - 连接到MQTT Broker并设置回调函数。 2. 主循环: - 每10分钟检查网络连接状态,如果未连接则尝试重连。 - 每30秒检查是否需要开启PM传感器,如果需要则开启并读取数据,然后关闭。 - 每30秒检查是否需要读取HCHO传感器数据,如果需要则读取。 - 每5秒检查是否需要读取其他传感器(温湿度、VOC、二氧化碳)数据,如果需要则读取并发送数据。 3. 数据处理: - 将传感器数据转换为字符串格式。 - 通过MQTT将数据发送到Home Assistant。 #### 5. 代码展示 本项目中使用到的库 | 库名 | 用途 | 项目地址 | | -------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | | Adafruit SHT4x Library | SHT4X 数字湿度 + 温度传感器的库。 | [adafruit/Adafruit_SHT4X: Arduino driver for Adafruit SHT4X temperature / humidity breakout (github.com)](https://github.com/adafruit/Adafruit_SHT4x) | | WZ Library | 面向`达特WZ-S`、`普晟WZ-H3`、`炜盛ZE08-CH2O`系列甲醛传感器的Arduino开发库 | https://github.com/leonlucc/WZ | | PMS Library | 用于 Plantower PMS 传感器的 Arduino 库。 支持 PMS x003 传感器(1003、3003、5003、6003、7003)。 | [fu-hsi/PMS: Arduino library for Plantower PMS x003 family sensors. (github.com)](https://github.com/fu-hsi/pms) | | Sensirion I2C SCD4x | 这是使用 I2C 接口的 Arduino 的 Sensirion SCD4x 库。 | [Sensirion/arduino-i2c-scd4x: Arduino library for Sensirion SCD4x sensors (github.com)](https://github.com/Sensirion/arduino-i2c-scd4x) | | ENS160 - Adafruit Fork | 用于ENS160气体传感器的库。 | [adafruit/ENS160_driver: Driver for the ScioSense ENS160 digital gas sensor (github.com)](https://github.com/adafruit/ENS160_driver) | | home-assistant-integration | ArduinoHA 允许使用 MQTT 将基于 Arduino/ESP 的设备与 Home Assistant 集成。 | [dawidchyrzynski/arduino-home-assistant: ArduinoHA 允许使用 MQTT 将基于 Arduino/ESP 的设备与 Home Assistant 集成。 (github.com)](https://github.com/dawidchyrzynski/arduino-home-assistant) | Follow_me2_expand_task.ino ``` c++ #include "WiFiS3.h" #include "SPI.h" #include "Adafruit_SHT4x.h" #include "WZ.h" #include "SoftwareSerial.h" #include "ScioSense_ENS160.h" #include "PMS.h" #include "SensirionI2CScd4x.h" #include "ArduinoHA.h" #include "arduino_secrets.h" #include "arduino_mqtt.h" char sta_ssid[] = SECRET_STA_SSID; // your network SSID (name) char sta_pass[] = SECRET_STA_PASS; // your network password (use for WPA, or use as key for WEP) char addr[] = MQTT_BROKER_ADDR; int port = MQTT_BROKER_PORT; char username[] = MQTT_BROKER_USERNAME; char password[] = MQTT_BROKER_PASSWORD; int status = WL_IDLE_STATUS; const byte PIN_RX = 3; const byte PIN_TX = 2; // Sensor read intervals (in milliseconds) const unsigned long sensorAStartInterval = 30000; // pm Sensor read intervals 60s const unsigned long sensorAReadDuration = 60000; // pm Sensor read intervals 60s const unsigned long sensorBInterval = 30000; // hcho Sensor read intervals 60s const unsigned long sensorCInterval = 5000; // other Sensor read intervals 5s const unsigned long reconnectInterval = 600000; // Last time the sensors were read unsigned long previousMillisA = 0; unsigned long previousMillisB = 0; unsigned long previousMillisC = 0; unsigned long previousMillisReconnect = 0; bool sensorActive = false; WiFiClient client; // Arduino Home Assistant integration HADevice device("aiaq"); //HADevice device(mac, sizeof(mac)); HAMqtt mqtt(client, device); Adafruit_SHT4x sht4 = Adafruit_SHT4x(); SensirionI2CScd4x scd4x; ScioSense_ENS160 ens160(ENS160_I2CADDR_0); SoftwareSerial WzSoftSerial(PIN_RX, PIN_TX); WZ wz(WzSoftSerial); WZ::DATA hcho_data; PMS pms(Serial1); PMS::DATA data; HASensor sht4_temperature_sensor("sht4_temperature_sensor"); HASensor sht4_relative_humidity_sensor("sht4_relative_humidity_sensor"); HASensor pms7003_pm1_sensor("pms7003_pm1_sensor"); HASensor pms7003_pm2_5_sensor("pms7003_pm2_5_sensor"); HASensor pms7003_pm10_sensor("pms7003_pm10_sensor"); HASensor wz_h3_hcho_ppd_sensor("wz_h3_hcho_ppd_sensor"); HASensor wz_h3_hcho_ugm3_sensor("wz_h3_hcho_ugm3_sensor"); HASensor scd4_co2_sensor("co2"); HASensor ens160_aqi_sensor("aqi"); HASensor ens160_tvoc_sensor("tvoc"); HASensor ens160_eco2_sensor("eco2"); void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); while (!Serial) delay(10); Adafruit_SHT4x_Init(); WZ_Init(); ENS160_Init(); PMS_Init(); SCD41_Init(); reconnect(); device.setName("aiaq"); device.setSoftwareVersion("1.0.0"); sht4_temperature_sensor.setIcon("mdi:home"); sht4_temperature_sensor.setName("Temperature"); sht4_temperature_sensor.setUnitOfMeasurement("°C"); sht4_relative_humidity_sensor.setIcon("mdi:home"); sht4_relative_humidity_sensor.setName("Humidity"); sht4_relative_humidity_sensor.setUnitOfMeasurement("%"); pms7003_pm1_sensor.setIcon("mdi:home"); pms7003_pm1_sensor.setName("PM1"); pms7003_pm1_sensor.setUnitOfMeasurement("ug/m3"); pms7003_pm2_5_sensor.setIcon("mdi:home"); pms7003_pm2_5_sensor.setName("PM2.5"); pms7003_pm2_5_sensor.setUnitOfMeasurement("ug/m3"); pms7003_pm10_sensor.setIcon("mdi:home"); pms7003_pm10_sensor.setName("PM10"); pms7003_pm10_sensor.setUnitOfMeasurement("ug/m3"); wz_h3_hcho_ppd_sensor.setIcon("mdi:home"); wz_h3_hcho_ppd_sensor.setName("hcho"); wz_h3_hcho_ppd_sensor.setUnitOfMeasurement("ppd"); wz_h3_hcho_ugm3_sensor.setIcon("mdi:home"); wz_h3_hcho_ugm3_sensor.setName("hcho"); wz_h3_hcho_ugm3_sensor.setUnitOfMeasurement("ugm3"); scd4_co2_sensor.setIcon("mdi:home"); scd4_co2_sensor.setName("Co2"); scd4_co2_sensor.setUnitOfMeasurement("ppm"); ens160_aqi_sensor.setIcon("mdi:home"); ens160_aqi_sensor.setName("AQI"); ens160_aqi_sensor.setUnitOfMeasurement(""); ens160_eco2_sensor.setIcon("mdi:home"); ens160_eco2_sensor.setName("eCo2"); ens160_eco2_sensor.setUnitOfMeasurement("ppm"); ens160_tvoc_sensor.setIcon("mdi:home"); ens160_tvoc_sensor.setName("TVOC"); ens160_tvoc_sensor.setUnitOfMeasurement("ppb"); mqtt.onMessage(onMqttMessage); mqtt.onConnected(onMqttConnected); mqtt.onDisconnected(onMqttDisconnected); mqtt.onStateChanged(onMqttStateChanged); mqtt.setKeepAlive(60); mqtt.begin(addr,port,username,password); } void loop() { unsigned long currentMillis = millis(); mqtt.loop(); char pm1buffer[10]; char pm25buffer[10]; char pm10buffer[10]; char ppdbuffer[10]; char ugm3buffer[10]; char tempbuffer[10]; char humibuffer[10]; char aqibuffer[10]; char tvocbuffer[10]; char eco2buffer[10]; char co2buffer[10]; // 非阻塞检查网络连接并重连 10min if (currentMillis - previousMillisReconnect >= reconnectInterval) { previousMillisReconnect = currentMillis; if (!client.connected()){ reconnect(); } } // 非阻塞开启PM传感器 30s if (!sensorActive && currentMillis - previousMillisA >= sensorAStartInterval) { previousMillisA = currentMillis; pms.wakeUp(); sensorActive = true; } // 非阻塞读取PM传感器数据 60s 并关闭 if (sensorActive && currentMillis - previousMillisA >= sensorAReadDuration) { pms.requestRead(); if (pms.readUntil(data)) { digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH); Serial.print("PM 1.0 (ug/m3): "); Serial.println(data.PM_AE_UG_1_0); Serial.print("PM 2.5 (ug/m3): "); Serial.println(data.PM_AE_UG_2_5); Serial.print("PM 10.0 (ug/m3): "); Serial.println(data.PM_AE_UG_10_0); dtostrf(data.PM_AE_UG_1_0, 6, 2, pm1buffer); dtostrf(data.PM_AE_UG_2_5,6,2,pm25buffer); dtostrf(data.PM_AE_UG_10_0, 6, 2, pm10buffer); pms7003_pm1_sensor.setValue(pm1buffer); pms7003_pm2_5_sensor.setValue(pm25buffer); pms7003_pm10_sensor.setValue(pm10buffer); } else{ Serial.println("PM Sensor No data."); } pms.sleep(); digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, LOW); sensorActive = false; } // 非阻塞读取HCHO传感器数据 30s if (currentMillis - previousMillisB >= sensorBInterval) { previousMillisB = currentMillis; digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH); // 获取甲醛传感器WZ-H3-NK数据 wz.requestRead(); if (wz.readUntil(hcho_data)) { Serial.print("HCHO (ppd): "); Serial.println(hcho_data.HCHO_PPB); Serial.print("HCHO (ug/m3): "); Serial.println(hcho_data.HCHO_UGM3); dtostrf(hcho_data.HCHO_PPB, 6, 2, ppdbuffer); dtostrf(hcho_data.HCHO_UGM3, 6, 2, ugm3buffer); wz_h3_hcho_ppd_sensor.setValue(ppdbuffer); wz_h3_hcho_ugm3_sensor.setValue(ugm3buffer); } digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, LOW); } // 非阻塞读取其他传感器数据 5s if (currentMillis - previousMillisC >= sensorCInterval) { previousMillisC = currentMillis; digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH); // 获取温湿度传感器sht40数据 sensors_event_t humi, temp; sht4.getEvent(&humi, &temp); Serial.print("Temperature: "); Serial.print(temp.temperature); Serial.println("℃"); Serial.print("Humidity: "); Serial.print(humi.relative_humidity); Serial.println("% rH"); dtostrf(temp.temperature, 6, 2, tempbuffer); dtostrf(humi.relative_humidity, 6, 2, humibuffer); sht4_temperature_sensor.setValue(tempbuffer); sht4_relative_humidity_sensor.setValue(humibuffer); // 获取VOC传感器 if (ens160.available()) { ens160.measure(true); ens160.measureRaw(true); Serial.print("AQI: "); Serial.println(ens160.getAQI()); Serial.print("TVOC: "); Serial.print(ens160.getTVOC()); Serial.println("ppb"); Serial.print("eCO2: "); Serial.print(ens160.geteCO2()); Serial.println("ppm"); dtostrf(ens160.getAQI(), 6, 2, aqibuffer); dtostrf(ens160.getTVOC(), 6, 2, tvocbuffer); dtostrf(ens160.geteCO2(), 6, 2, eco2buffer); ens160_aqi_sensor.setValue(aqibuffer); ens160_tvoc_sensor.setValue(tvocbuffer); ens160_eco2_sensor.setValue(eco2buffer); } // 获取二氧化碳传感器 uint16_t error; char errorMessage[256]; // Read Measurement uint16_t co2 = 0; float temperature = 0.0f; float humidity = 0.0f; bool isDataReady = false; error = scd4x.getDataReadyFlag(isDataReady); if (error) { Serial.print("Error trying to execute getDataReadyFlag(): "); errorToString(error, errorMessage, 256); Serial.println(errorMessage); return; } if (!isDataReady) { return; } error = scd4x.readMeasurement(co2, temperature, humidity); if (error) { Serial.print("Error trying to execute readMeasurement(): "); errorToString(error, errorMessage, 256); Serial.println(errorMessage); } else if (co2 == 0) { Serial.println("Invalid sample detected, skipping."); } else { Serial.print("Co2:"); Serial.println(co2); dtostrf(co2, 6, 2, co2buffer); scd4_co2_sensor.setValue(co2buffer); digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, LOW); } } } void reconnect() { Serial.print("Attempting to connect to SSID: "); Serial.print(sta_ssid); int i = 0; while (status != WL_CONNECTED) { Serial.print("."); status = WiFi.begin(sta_ssid, sta_pass); i++; if (status == WL_CONNECTED){ Serial.println("Connected to WiFi successfully"); //Serial.println(WiFi.localIP()); break; } if(i == 5) break; delay(5000); } } void onMqttMessage(const char* topic, const uint8_t* payload, uint16_t length) { // This callback is called when message from MQTT broker is received. // Please note that you should always verify if the message's topic is the one you expect. // For example: if (memcmp(topic, "myCustomTopic") == 0) { ... } Serial.print("New message on topic: "); Serial.println(topic); Serial.print("Data: "); Serial.println((const char*)payload); } void onMqttConnected() { Serial.println("Connected to the broker!"); } void onMqttDisconnected() { Serial.println("Disconnected from the broker!"); } void onMqttStateChanged(HAMqtt::ConnectionState state) { Serial.print("MQTT state changed to: "); Serial.println(static_cast(state)); } void Adafruit_SHT4x_Init() { Serial.println("Adafruit SHT4x Initializing..."); if (!sht4.begin(&Wire1)) { Serial.println("Couldn't find SHT4x"); while (1) delay(1); } Serial.println("Found SHT4x sensor"); Serial.print("Serial number 0x"); Serial.println(sht4.readSerial(), HEX); // You can have 3 different precisions, higher precision takes longer sht4.setPrecision(SHT4X_HIGH_PRECISION); switch (sht4.getPrecision()) { case SHT4X_HIGH_PRECISION: Serial.println("High precision"); break; case SHT4X_MED_PRECISION: Serial.println("Med precision"); break; case SHT4X_LOW_PRECISION: Serial.println("Low precision"); break; } // You can have 6 different heater settings // higher heat and longer times uses more power // and reads will take longer too! sht4.setHeater(SHT4X_NO_HEATER); switch (sht4.getHeater()) { case SHT4X_NO_HEATER: Serial.println("No heater"); break; case SHT4X_HIGH_HEATER_1S: Serial.println("High heat for 1 second"); break; case SHT4X_HIGH_HEATER_100MS: Serial.println("High heat for 0.1 second"); break; case SHT4X_MED_HEATER_1S: Serial.println("Medium heat for 1 second"); break; case SHT4X_MED_HEATER_100MS: Serial.println("Medium heat for 0.1 second"); break; case SHT4X_LOW_HEATER_1S: Serial.println("Low heat for 1 second"); break; case SHT4X_LOW_HEATER_100MS: Serial.println("Low heat for 0.1 second"); break; } Serial.println("Adafruit SHT4x Initialization Completed"); } void WZ_Init() { Serial.println("WZ Initializing..."); WzSoftSerial.begin(9600); wz.passiveMode(); Serial.println("WZ Initialization Completed"); } void ENS160_Init() { Serial.println("ENS160 Initializing..."); ens160.begin(); Serial.println(ens160.available() ? "done." : "failed!"); if (ens160.available()) { // Print ENS160 versions Serial.print("\tRev: "); Serial.print(ens160.getMajorRev()); Serial.print("."); Serial.print(ens160.getMinorRev()); Serial.print("."); Serial.println(ens160.getBuild()); Serial.print("\tStandard mode "); Serial.println(ens160.setMode(ENS160_OPMODE_STD) ? "done." : "failed!"); } Serial.println("ENS160 Initialization Completed"); } void PMS_Init() { Serial.println("PMS7003 Initializing..."); Serial1.begin(9600); pms.passiveMode(); Serial.println("PMS7003 Initialization Completed"); } void SCD41_Init() { Serial.println("SCD41 Initializing..."); uint16_t error; char errorMessage[256]; scd4x.begin(Wire); // stop potentially previously started measurement error = scd4x.stopPeriodicMeasurement(); if (error) { Serial.print("Error trying to execute stopPeriodicMeasurement(): "); errorToString(error, errorMessage, 256); Serial.println(errorMessage); } uint16_t serial0; uint16_t serial1; uint16_t serial2; error = scd4x.getSerialNumber(serial0, serial1, serial2); if (error) { Serial.print("Error trying to execute getSerialNumber(): "); errorToString(error, errorMessage, 256); Serial.println(errorMessage); } else { printSerialNumber(serial0, serial1, serial2); } // Start Measurement error = scd4x.startPeriodicMeasurement(); if (error) { Serial.print("Error trying to execute startPeriodicMeasurement(): "); errorToString(error, errorMessage, 256); Serial.println(errorMessage); } Serial.println("SCD41 Initialization Completed"); } void printUint16Hex(uint16_t value) { Serial.print(value < 4096 ? "0" : ""); Serial.print(value < 256 ? "0" : ""); Serial.print(value < 16 ? "0" : ""); Serial.print(value, HEX); } void printSerialNumber(uint16_t serial0, uint16_t serial1, uint16_t serial2) { Serial.print("Serial: 0x"); printUint16Hex(serial0); printUint16Hex(serial1); printUint16Hex(serial2); Serial.println(); } ``` arduino_mqtt.h ``` c++ // MQTT服务链接 #define MQTT_BROKER_ADDR "emqx.inversedesign.net" // 这里输入你的mqtt服务器地址 #define MQTT_BROKER_PORT 1883 #define MQTT_BROKER_USERNAME "aiaq" #define MQTT_BROKER_PASSWORD "aiaq" ``` arduino_secrets.h ``` c++ // 双引号中输入你的 WIFI 账号密码 #define SECRET_STA_SSID "" #define SECRET_STA_PASS "" ``` #### 6. 视频演示 [localvideo]ecd254ffff57c0fc6221bfab607a4ced[/localvideo] ## 总结 通过本次活动,尝试了自己绘制PCB板、打样、焊接。对贴片元件焊接也初步上手。虽然过程还是很艰难。焊废了几块板子,之前竟敢挑战焊接0201的电阻。也是险些看瞎了眼儿了。通过本次活动对Arduino开发板以及Arduino IDE有了基本了解,后续在学习开发板有了更多的选择。希望能多多参与学习活动,也再次希望Follow me活动越办越好。
-
上传了资料: 【Follow me第二季第2期】智能家庭空气质量监测仪
-
加入了学习《Follow me 第二季第2期任务提交》,观看 【得捷电子Follow me】提交视频
-
加入了学习《【Follow me第二季第2期】Arduino UNO R4 WiF》,观看 【Follow me第二季第2期】Arduino UNO R4 WiF
-
加入了学习《FollowMe 第二季:2 - Arduino UNO R4 Wi-Fi 及任务讲解》,观看 Arduino UNO R4 Wi-Fi 及任务讲解
- 2024-09-21
-
加入了学习《直播回放: FollowMe 3 与得捷一起解锁开发板的超能力》,观看 FollowMe 3 与得捷一起解锁开发板的超能力
-
加入了学习《FollowMe 第二季: 1 Adafruit Circuit Playground Express及任务讲解》,观看 Adafruit Circuit Playground Express 及任务讲解
- 2024-02-18
-
回复了主题帖: 【得捷电子Follow me第4期】成果展示汇总帖
Jacktang 发表于 2024-2-18 07:33 用杜邦线来连接DS3231和屏幕也是一样的正常显示,,, 嗯 我索性就全部用杜邦线连接了 ,当时咋没想到DS3231可以跟屏幕插在一块
- 2024-02-17
-
发表了主题帖: 【得捷电子Follow me第4期】成果展示汇总帖
**首先感谢 DigiKey得捷 | 电子工程世界EEWorld 举办的Follow me活动,与得捷电子一起解锁开发板的超能力!** # 前言 **龙年新春到,福气满天飘。愿所有看到此贴的人事业如龙腾飞跃,财源似龙脉绵长。家庭和睦如龙凤呈祥,身体健康赛龙马精神。祝你在新的一年里,龙运亨通,万事如意!**:Onion-54: :Onion-54: :Onion-54: # 项目介绍 本项目包含以下内容: 入门任务:开发环境搭建,BLINK,驱动液晶显示器进行显示(没有则串口HelloWorld) 搭配器件: [W5500-EVB-Pico](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/wiznet/W5500-EVB-PICO/16515824)、 [Adafruit Sharp Memory Display Breakout](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/adafruit-industries-llc/3502/7386264) 基础任务一:完成主控板W5500初始化(静态IP配置),并能使用局域网电脑ping通,同时W5500可以ping通互联网站点;通过抓包软件(Wireshark、Sniffer等)抓取本地PC的ping报文,展示并分析。 搭配器件: [W5500-EVB-Pico](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/wiznet/W5500-EVB-PICO/16515824)、 [Adafruit Sharp Memory Display Breakout](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/adafruit-industries-llc/3502/7386264) 基础任务二:主控板建立TCPIP或UDP服务器,局域网PC使用TCPIP或UDP客户端进行连接并发送数据,主控板接收到数据后,送液晶屏显示(没有则通过串口打印显示);通过抓包软件抓取交互报文,展示并分析。(TCP和UDP二选一,或者全都操作) 搭配器件: [W5500-EVB-Pico](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/wiznet/W5500-EVB-PICO/16515824)、 [Adafruit Sharp Memory Display Breakout](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/adafruit-industries-llc/3502/7386264) 进阶任务:从NTP服务器(注意数据交互格式的解析)同步时间,获取时间送显示屏(串口)显示。 搭配器件: [W5500-EVB-Pico](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/wiznet/W5500-EVB-PICO/16515824)、 [Adafruit Sharp Memory Display Breakout](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/adafruit-industries-llc/3502/7386264) 终极任务(二选一) ■ **终极任务一:**访问 [https://www.digikey.cn/zh/resources/api-solutions](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/resources/api-solutions),以了解得捷(DigiKey)数字化解决方案及其API操作,设计一款DigiKey电子元器件价格及库存监视器,能实时同步并显示指定,电子元器件的价格、库存等信息。 ■ **终极任务二:**使用外部存储器,组建简易FTP文件服务器,并能正常上传下载文件。 搭配器件: [W5500-EVB-Pico](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/wiznet/W5500-EVB-PICO/16515824)、 [Adafruit Sharp Memory Display Breakout](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/adafruit-industries-llc/3502/7386264) 本项目视频及源码: - 视频 [【得捷Follow me第4期】+ 任务成果视频展示](https://training.eeworld.com.cn/video/39268) - 源码 [【得捷Follow me第4期】+ 任务成果代码展示](https://download.eeworld.com.cn/detail/shazhongjin/631134) # 开箱展示 购买的配件有: [W5500-EVB-Pico](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/wiznet/W5500-EVB-PICO/16515824) [MICROSD CARD BFF QT PY/XIAO|](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/seeed-technology-co-ltd/103100142/13688265) [Pico LCD 1.14](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/seeed-technology-co-ltd/103030400/14317043) [Pico RTC DS3231](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/seeed-technology-co-ltd/103030398/14317036) 开箱全家福: # 任务成果展示及说明 ## 入门任务 开发环境搭建,BLINK,驱动液晶显示器进行显示(没有则串口HelloWorld) ### 一、硬件介绍 | 硬件 | 链接、资料 | 图片 | | -------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------- | | W5500-EVB-Pico | [W5500-EVB-PICO WIZnet 开发板 套件 编程器 DigiKey](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/wiznet/W5500-EVB-PICO/16515824) [W5500-EVB-Pico WIZnet Document System](https://docs.wiznet.io/Product/iEthernet/W5500/w5500-evb-pico) |  | | Pico LCD 1.14 | [103030400 Seeed Technology Co., Ltd 开发板 套件 编程器 DigiKey](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/seeed-technology-co-ltd/103030400/14317043) [Pico LCD 1.14 - Waveshare Wiki](https://www.waveshare.com/wiki/Pico-LCD-1.14) |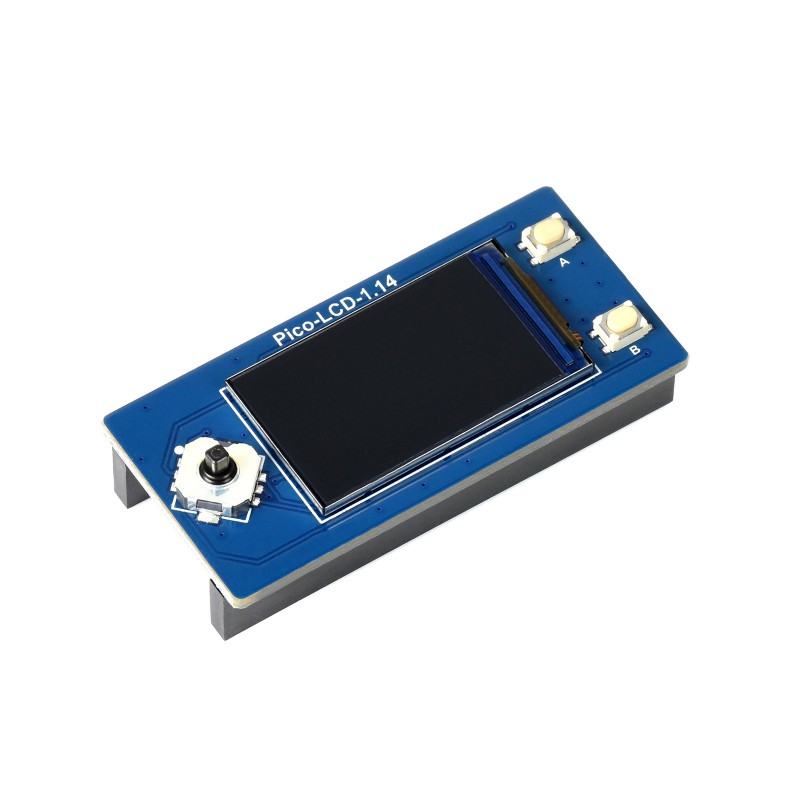  | ### 二、搭建开发环境 本项目使用MicroPython进行开发。 1. 下载 Wiznet W5500-EVB-Pico MicroPython固件 [MicroPython - Python for microcontrollers](https://micropython.org/download/W5500_EVB_PICO/) 2. 按住核心板的boot键并连接数据线到电脑,或者已连接电脑状态下按住boot键再按下Run(reset)键。然后将下载的固件应复制到出现的 USB 大容量存储设备中,新固件将自动写入并复位。 3. 将Wiznet W5500-EVB-Pico焊接排针,Pico LCD 1.14 显示模块与Wiznet W5500-EVB-Pico进行连接。需要注意的是核心板焊接排针的方向及与显示模块的针脚的对应。 ### 三、代码展示 /beginner_task_code.py ``` python import LCD_1inch14,time from machine import Pin,SPI led = Pin(25, Pin.OUT) if __name__=='__main__': lcd = LCD_1inch14.LCD() lcd.WriteLine('Follow Me 4') lcd.WriteLine('by shazhongjin') lcd.WriteLine('Hello World!') while True: led.value(1) lcd.WriteLine("LED ON") time.sleep(1) led.value(0) lcd.WriteLine("LED OFF") time.sleep(1) ``` 本项目使用到的LCD_1inch14库为根据微雪例程 [Demo codes](https://files.waveshare.com/upload/2/28/Pico_code.7z) , 屏幕显示参考Follow me 2中Adafruit ESP32-S3 TFT Feather 开发板 刷入CircuitPython的屏幕显示效果来对此库进行调整。设计思路如下: 项目中所有用到屏幕的任务均使用该库,后续不在提及。 /lib/LCD_1inch14.py ``` python from machine import Pin,SPI,PWM import framebuf,time BL = 13 DC = 8 RST = 12 MOSI = 11 SCK = 10 CS = 9 Row = 1 class LCD(framebuf.FrameBuffer): def __init__(self): self.width = 240 self.height = 135 self.cs = Pin(CS,Pin.OUT) self.rst = Pin(RST,Pin.OUT) self.cs(1) self.spi = SPI(1) self.spi = SPI(1,1000_000) self.spi = SPI(1,10000_000,polarity=0, phase=0,sck=Pin(SCK),mosi=Pin(MOSI),miso=None) self.dc = Pin(DC,Pin.OUT) self.dc(1) self.buffer = bytearray(self.height * self.width * 2) super().__init__(self.buffer, self.width, self.height, framebuf.RGB565) self.init_display() self.red = 0x07E0 self.green = 0x001f self.blue = 0xf800 self.white = 0xffff self.black = 0x0000 def write_cmd(self, cmd): self.cs(1) self.dc(0) self.cs(0) self.spi.write(bytearray([cmd])) self.cs(1) def write_data(self, buf): self.cs(1) self.dc(1) self.cs(0) self.spi.write(bytearray([buf])) self.cs(1) def init_display(self): """Initialize dispaly""" self.rst(1) self.rst(0) self.rst(1) self.write_cmd(0x36) self.write_data(0x70) self.write_cmd(0x3A) self.write_data(0x05) self.write_cmd(0xB2) self.write_data(0x0C) self.write_data(0x0C) self.write_data(0x00) self.write_data(0x33) self.write_data(0x33) self.write_cmd(0xB7) self.write_data(0x35) self.write_cmd(0xBB) self.write_data(0x19) self.write_cmd(0xC0) self.write_data(0x2C) self.write_cmd(0xC2) self.write_data(0x01) self.write_cmd(0xC3) self.write_data(0x12) self.write_cmd(0xC4) self.write_data(0x20) self.write_cmd(0xC6) self.write_data(0x0F) self.write_cmd(0xD0) self.write_data(0xA4) self.write_data(0xA1) self.write_cmd(0xE0) self.write_data(0xD0) self.write_data(0x04) self.write_data(0x0D) self.write_data(0x11) self.write_data(0x13) self.write_data(0x2B) self.write_data(0x3F) self.write_data(0x54) self.write_data(0x4C) self.write_data(0x18) self.write_data(0x0D) self.write_data(0x0B) self.write_data(0x1F) self.write_data(0x23) self.write_cmd(0xE1) self.write_data(0xD0) self.write_data(0x04) self.write_data(0x0C) self.write_data(0x11) self.write_data(0x13) self.write_data(0x2C) self.write_data(0x3F) self.write_data(0x44) self.write_data(0x51) self.write_data(0x2F) self.write_data(0x1F) self.write_data(0x1F) self.write_data(0x20) self.write_data(0x23) self.write_cmd(0x21) self.write_cmd(0x11) self.write_cmd(0x29) # 初始化内容 Row = 1 self.fill(0x0000) self.text("MicroPython",20,4,0xffff) self.fill_rect(1,1,3,13,0xffff) self.fill_rect(4,1,1,2,0xffff) self.fill_rect(5,1,2,13,0xffff) self.fill_rect(7,11,2,3,0xffff) self.fill_rect(8,1,2,13,0xffff) self.fill_rect(10,1,1,2,0xffff) self.fill_rect(11,1,3,13,0xffff) self.fill_rect(12,10,1,3,0x0000) self.show() def show(self): self.write_cmd(0x2A) self.write_data(0x00) self.write_data(0x28) self.write_data(0x01) self.write_data(0x17) self.write_cmd(0x2B) self.write_data(0x00) self.write_data(0x35) self.write_data(0x00) self.write_data(0xBB) self.write_cmd(0x2C) self.cs(1) self.dc(1) self.cs(0) self.spi.write(self.buffer) self.cs(1) def Clean(self): self.init_display() def WriteLine(self, s : str): import math global Row #print(f'print string is : {s}') length = len(s) #print(f'string length is : {length}') rownum= math.ceil(length / 30) #print(f'string rows : {rownum}') for i in range(rownum): i += 1 print(s[30 * (i - 1) :30 * i]) # 渲染头部 self.fill_rect(0,0,350,15,0x0000) self.text("MicroPython",20,4,0xffff) self.fill_rect(1,1,3,13,0xffff) self.fill_rect(4,1,1,2,0xffff) self.fill_rect(5,1,2,13,0xffff) self.fill_rect(7,11,2,3,0xffff) self.fill_rect(8,1,2,13,0xffff) self.fill_rect(10,1,1,2,0xffff) self.fill_rect(11,1,3,13,0xffff) self.fill_rect(12,10,1,3,0x0000) # 当i大于12行时屏幕开始滚动 #print(f'screen rows : {Row}') if (Row > 10): self.scroll(0,-1 * 12) self.fill_rect(0,124,350, 10 ,0x0000) # 渲染头部 self.fill_rect(0,0,350,15,0x0000) self.text("MicroPython",20,4,0xffff) self.fill_rect(1,1,3,13,0xffff) self.fill_rect(4,1,1,2,0xffff) self.fill_rect(5,1,2,13,0xffff) self.fill_rect(7,11,2,3,0xffff) self.fill_rect(8,1,2,13,0xffff) self.fill_rect(10,1,1,2,0xffff) self.fill_rect(11,1,3,13,0xffff) self.fill_rect(12,10,1,3,0x0000) if (Row < 10): self.text(s[30 * (i - 1) :30 * i], 0 , 15 + (Row-1) * 12 + 2 ,0xffff); else: self.text(s[30 * (i - 1) :30 * i], 0 , 15 + (10-1) * 12 + 2 ,0xffff); Row += 1 self.show() #print('\n') ``` ### 四、演示 [localvideo]479d9fdcb8e023da04f4ed99d0a71679[/localvideo] --- 参考资料: [W5500-EVB-Pico | WIZnet Document System](https://docs.wiznet.io/Product/iEthernet/W5500/w5500-evb-pico) [Pico LCD 1.14 - Waveshare Wiki](https://www.waveshare.com/wiki/Pico-LCD-1.14) ## 基础任务一 完成主控板W5500初始化(静态IP配置),并能使用局域网电脑ping通,同时W5500可以ping通互联网站点;通过抓包软件(Wireshark、Sniffer等)抓取本地PC的ping报文,展示并分析。 ### 一、W5500初始化并配置静态IP 根据WiZnet官方例程,配置静态IP先要查询当前网络网关(比如当前网络网关为192.168.1.1),使用`nic.ifconfig(('IP','子网掩码','网关','DNS'))`来配置w5500的静态ip地址。如下例程: ``` python from machine import Pin,SPI spi=SPI(0,2_000_000, mosi=Pin(19),miso=Pin(16),sck=Pin(18)) nic = network.WIZNET5K() #spi,cs,reset pin # network.WIZNET5K(spi,Pin(17),Pin(20)) nic.active(True) # 设置动态ip #nic.ifconfig('dhcp') # 设置静态ip nic.ifconfig(('192.168.1.107','255.255.255.0','192.168.1.1','8.8.8.8')) while not nic.isconnected(): time.sleep(1) print(nic.ifconfig()) ``` ### 二、使用局域网电脑ping通W5500-EVB-Pico,并使用Wireshark抓包ping报文 ping命令通常被用来测试网络连接,可以帮助你确定电脑是否能够通过IP地址访问另一台电脑。当你执行ping命令时,它会发送一个小数据包到特定的IP地址上,并等待响应。如果连接成功,你会看到回复的时间以及数据包是否成功送达。 运行ping命令 地址192.168.1.108 双击数据表列表,查看数据包各层详细信息。 互联网层IP包头部信息 传输层ICMP协议信息 ### 三、使用W5500-EVB-Pico ping通局域网中的电脑 在gitee中找到一个uping的仓库,可以实现像电脑中的Ping命令一样在开发板中运行ping命令。由于该库中将ping信息输出到控制台上。再此也是做了小小的改动将信息输出到屏幕上,详见下节代码展示。 ### 四、代码展示 /basic_task1_code.py ``` python from machine import Pin,SPI,RTC import time,network,uping import LCD_1inch14 #W5x00 chip init def w5x00_init(): spi=SPI(0,2_000_000, mosi=Pin(19),miso=Pin(16),sck=Pin(18)) nic = network.WIZNET5K() #spi,cs,reset pin # spi,Pin(17),Pin(20) nic.active(True) # If you use the Dynamic IP(DHCP), you must use the "nic.ifconfig('dhcp')". #nic.ifconfig('dhcp') # If you use the Static IP, you must use the "nic.ifconfig("IP","subnet","Gateway","DNS")". nic.ifconfig(('192.168.1.108','255.255.255.0','192.168.1.1','8.8.8.8')) while not nic.isconnected(): time.sleep(1) #print(nic.regs()) print(nic.ifconfig()) if __name__ == "__main__": lcd = LCD_1inch14.LCD() lcd.WriteLine('Follow Me 4') lcd.WriteLine('by shazhongjin') lcd.WriteLine('base task 1') w5x00_init() # 使用W5500 ping互联网站点 www.baidu.com ping = uping.Ping('www.baidu.com',COUNT=100,IsOutputScreen =True) ping.start() ``` /lib/uping.py ``` python ''' Author: Yogile Gitee: https://gitee.com/yogile Date: 2022-07-16 17:41:38 LastEditors: Yogile LastEditTime: 2022-07-16 18:04:28 Fork from: https://github.com/coffee-it/uPing Description: Porting code to ESP32 chips ''' import utime import uselect import uctypes import usocket import ustruct import urandom import micropython import LCD_1inch14 urandom.seed(utime.ticks_us()) class Ping(): """ Create the ping calculating object exemplar """ def __init__(self, HOST, SOURCE=None, COUNT=4, INTERVAL=1000, SIZE=64, TIMEOUT=5000, quiet=False, IsOutputScreen = False): self.HOST = HOST self.COUNT = COUNT self.TIMEOUT = TIMEOUT self.INTERVAL = INTERVAL self.SIZE = SIZE self.quiet = quiet self.END = None self.IsOutputScreen = IsOutputScreen # prepare packet assert SIZE >= 16, "pkt size too small" self._PKT = b'Q'*SIZE self.PKT_DESC = { "type": uctypes.UINT8 | 0, "code": uctypes.UINT8 | 1, "checksum": uctypes.UINT16 | 2, "id": uctypes.UINT16 | 4, "seq": uctypes.INT16 | 6, "timestamp": uctypes.UINT64 | 8, } # packet header descriptor h = uctypes.struct(uctypes.addressof(self._PKT), self.PKT_DESC, uctypes.BIG_ENDIAN) h.type = 8 # ICMP_ECHO_REQUEST h.code = 0 h.checksum = 0 h.id = urandom.getrandbits(16) h.seq = 1 self.h = h # init socket sock = usocket.socket(usocket.AF_INET, usocket.SOCK_RAW, 1) if SOURCE: src_addr = usocket.getaddrinfo(SOURCE, 1)[0][-1] # ip address sock.bind(src_addr) sock.setblocking(0) sock.settimeout(TIMEOUT/1000) addresses = usocket.getaddrinfo(HOST, 1) # [0][-1] # list of ip addresses assert addresses, "Can not take the IP address of host" self.CLIENT_IP = None for addr in addresses: try: sock.connect(addr[-1]) self.CLIENT_IP = addr[-1][0] except: continue assert self.CLIENT_IP, "Connection failed" self.sock = sock # [ COUNTERS ] self.seq_num = 1 # Next sequence number self.transmitted = 0 self.received = 0 self.seqs = None # LCD self.LCD = LCD_1inch14.LCD() def Output(self,msg :str): print(msg) if self.IsOutputScreen: self.LCD.WriteLine(msg) def start(self): """ Starting a ping cycle with the specified settings (like a interval, count e.t.c.) """ t = self.INTERVAL finish = False # [ Rtt metrics ] pongs = [] min_rtt, max_rtt = None, None # [ Start over ] self.seq_num = 1 self.transmitted = 0 self.received = 0 not self.quiet and self.Output("PING %s (%s): %u data bytes" % (self.HOST, self.CLIENT_IP, len(self._PKT))) if self.seqs: self.seqs.extend(list(range(self.seq_num, self.COUNT + 1))) # [seq_num, seq_num + 1, ...., seq_num + n]) else: self.seqs = list(range(self.seq_num, self.COUNT + 1)) # [1,2,...,count] # Здесь нужно подвязаться на реальное время while self.seq_num = self.INTERVAL: pong = self.ping() t = 0 rtt = pong[1] if rtt: pongs.append(rtt) if not min_rtt or rtt = max_rtt: max_rtt = round(rtt, 3) if len(self.seqs) == 0: finish = True if finish: break utime.sleep_ms(1) t += 1 losses = round((self.transmitted - self.received) / self.transmitted) * 100 avg_rtt = round(sum(pongs) / len(pongs), 3) if pongs else None from ucollections import namedtuple _result = namedtuple("result", ("tx", "rx", "losses", "min", "avg", "max")) result = _result(self.transmitted, self.received, losses, min_rtt, avg_rtt, max_rtt) if not self.quiet: self.Output(r'%u packets transmitted, %u packets received, %u packet loss' % (self.transmitted, self.received, losses)) if avg_rtt: self.Output(r'round-trip min/avg/max = %r/%r/%r ms' % (min_rtt, avg_rtt, max_rtt)) else: return result def ping(self): """ Send ping manually. Returns sequense number(int), round-trip time (ms, float), ttl """ sock = self.sock if not self.seqs: self.seqs = [] self.seqs.append(self.seq_num) seq, t_elasped, ttl = None, None, None # header h = self.h h.checksum = 0 h.seq = self.seq_num h.timestamp = utime.ticks_us() h.checksum = self.checksum(self._PKT) try: # send packet if sock.send(self._PKT) == self.SIZE: self.transmitted += 1 else: self.seqs.remove(self.seq_num) self.seq_num += 1 # recv packet while 1: resp = sock.recv(self.SIZE + 20) # ICMP header and payload + IP header resp_mv = memoryview(resp) h2 = uctypes.struct(uctypes.addressof(resp_mv[20:]), self.PKT_DESC, uctypes.BIG_ENDIAN) seq = h2.seq if h2.type==0 and h2.id==h.id and (seq in self.seqs): # 0: ICMP_ECHO_REPLY t_elasped = (utime.ticks_us()-h2.timestamp) / 1000 self.seqs.remove(seq) if h2.checksum == self.checksum(resp[24:]): # except IP header and a part of ICMP header (type, code, checksum) ttl = ustruct.unpack('!B', resp_mv[8:9])[0] # time-to-live self.received += 1 not self.quiet and self.Output("%u bytes from %s: icmp_seq=%u, ttl=%u, time=%f ms" % (len(resp[12:]), self.CLIENT_IP, seq, ttl, t_elasped)) break else: not self.quiet and self.Output("Payload checksum doesnt match") t_elasped = None break except Exception as identifier: import errno if identifier.args[0] == errno.EPIPE: self.Output("Client connection unexpectedly closed") pass elif identifier.args[0] == errno.EBADF: self.Output("Bad file descriptor.") pass else: raise identifier return (seq, t_elasped, ttl) async def ping_async(self): """ Send ping manually by async. Returns sequense number(int), round-trip time (ms, float), ttl """ sock = self.sock if not self.seqs: self.seqs = [] self.seqs.append(self.seq_num) seq, t_elasped, ttl = None, None, None # header h = self.h h.checksum = 0 h.seq = self.seq_num h.timestamp = utime.ticks_us() h.checksum = self.checksum(self._PKT) try: # send packet if sock.send(self._PKT) == self.SIZE: self.transmitted += 1 else: self.seqs.remove(self.seq_num) self.seq_num += 1 # recv packet while 1: resp = sock.recv(self.SIZE + 20) # ICMP header and payload + IP header resp_mv = memoryview(resp) h2 = uctypes.struct(uctypes.addressof(resp_mv[20:]), self.PKT_DESC, uctypes.BIG_ENDIAN) seq = h2.seq if h2.type==0 and h2.id==h.id and (seq in self.seqs): # 0: ICMP_ECHO_REPLY t_elasped = (utime.ticks_us()-h2.timestamp) / 1000 self.seqs.remove(seq) if h2.checksum == self.checksum(resp[24:]): # except IP header and a part of ICMP header (type, code, checksum) ttl = ustruct.unpack('!B', resp_mv[8:9])[0] # time-to-live self.received += 1 not self.quiet and self.Output("%u bytes from %s: icmp_seq=%u, ttl=%u, time=%f ms" % (len(resp[12:]), self.CLIENT_IP, seq, ttl, t_elasped)) break else: not self.quiet and self.Output("Payload checksum doesnt match") t_elasped = None break except Exception as identifier: import errno if identifier.args[0] == errno.EPIPE: self.Output("Client connection unexpectedly closed") pass elif identifier.args[0] == errno.EBADF: self.Output("Bad file descriptor.") pass else: raise identifier self.END = (seq, t_elasped, ttl) def checksum(self, data): if len(data) & 0x1: # Odd number of bytes data += b'\0' cs = 0 for pos in range(0, len(data), 2): b1 = data[pos] b2 = data[pos + 1] cs += (b1 = 0x10000: cs = (cs & 0xffff) + (cs >> 16) cs = ~cs & 0xffff return cs def getEND_async(self): """ get ping_async() result """ return self.END def __enter__(self): return self def __exit__(self, type, value, traceback): self.close() def close(self): self.sock.close() ``` ### 五、演示 [localvideo]13056f04db15d23721687675e57b6838[/localvideo] [localvideo]4724f024b7b39bf014110a9840f301d5[/localvideo] --- 参考资料: [Wiznet/RP2040-HAT-MicroPython (github.com)](https://github.com/Wiznet/RP2040-HAT-MicroPython) [uPing: 使用 MicroPython 适配 ESP32 的 ping 函数,支持异步。 (gitee.com)](https://gitee.com/Yogile/uPing) ## 基础任务二 主控板建立TCPIP或UDP服务器,局域网PC使用TCPIP或UDP客户端进行连接并发送数据,主控板接收到数据后,送液晶屏显示(没有则通过串口打印显示);通过抓包软件抓取交互报文,展示并分析。(TCP和UDP二选一,或者全都操作) ### 一、硬件介绍 | 硬件 | 链接、资料 | 图片 | | ---- | ---- | ---- | | W5500-EVB-Pico | [W5500-EVB-PICO WIZnet 开发板 套件 编程器 DigiKey](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/wiznet/W5500-EVB-PICO/16515824) [W5500-EVB-Pico WIZnet Document System](https://docs.wiznet.io/Product/iEthernet/W5500/w5500-evb-pico) |  | | GROVE SHIELD FOR PI PICO V1.0 | [103100142 Seeed Technology Co., Ltd 开发板 套件 编程器 DigiKey](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/seeed-technology-co-ltd/103100142/13688265) |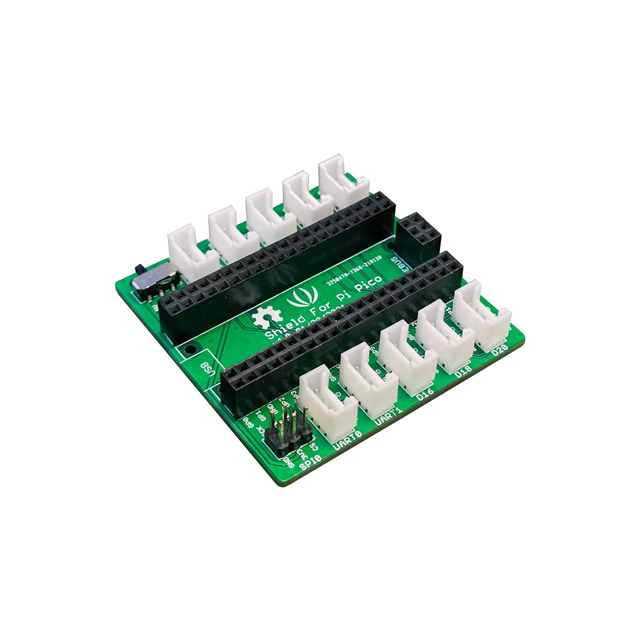  | | Grove - AHT20 I2C Industrial Grade Temperature&Humidity SensorF QT PY/XIAO | [101990644 Seeed Technology Co., Ltd 开发板 套件 编程器 DigiKey](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/seeed-technology-co-ltd/101990644/11681294) [Grove - AHT20 I2C Industrial Grade Temperature&Humidity Sensor Seeed Studio Wiki](https://wiki.seeedstudio.com/Grove-AHT20-I2C-Industrial-Grade-Temperature&Humidity-Sensor/) |  | ### 二、实现功能 本项目使用microdot来实现webapi服务器,来控制GPIO设备以及发送和接收数据。 1. 使用API来控制板载LED灯的开关; 2. 使用API获得Grove - AHT20设备的温度与湿度信息; 3. 使用API来实现一个聊天室的功能; ### 三、抓包分析 使用Wireshark软件对里聊天过程进行抓包分析,点击发送消息时向服务端发送一个Post请求将文本框中的内容发送给服务端。如下图所示可以看到数据包Info中 一个POST方法 路径为/send-message。通过查看Hypertext Transfer Protocol(应用层的信息)包括请求方法、请求路径、请求的完整路径等信息。在Javascript object Notation:application/json Json数据信息可以看到发送的内容“follow me4” 下图为客户端接收消息的数据包,可以看到Hypertext Transfer Protocol(应用层的信息)返回的200状态码,以及Json数据中返回的信息“Server received: follow me4”。 ### 三、代码展示 /basic_task2_code.py ``` python import network,os,time from usocket import socket from machine import Pin,SPI,SoftSPI from microdot import Microdot app = Microdot() led = Pin(25, Pin.OUT) addr = '' #w5500 初始化 def w5x00_init(): spi=SPI(0,2_000_000, mosi=Pin(19),miso=Pin(16),sck=Pin(18)) nic = network.WIZNET5K(spi,Pin(17),Pin(20)) #spi,cs,reset pin # network.WIZNET5K(spi,Pin(17),Pin(20)) nic.active(True) # If you use the Dynamic IP(DHCP), you must use the "nic.ifconfig('dhcp')". nic.ifconfig('dhcp') # If you use the Static IP, you must use the "nic.ifconfig("IP","subnet","Gateway","DNS")". #nic.ifconfig(('192.168.2.107','255.255.255.0','192.168.2.1','8.8.8.8')) while not nic.isconnected(): time.sleep(1) #print(nic.regs()) print(nic.ifconfig()) # Get connection IP global addr addr = nic.ifconfig()[0] def get_temp_humidity(debug = False): import ahtx0 from machine import I2C,SPI i2c = I2C(0, scl=Pin(9), sda=Pin(8)) # 获取传感器对象 sensor = ahtx0.AHT20(i2c) if debug: print("\nTemperature: %0.2f C" % sensor.temperature) print("Humidity: %0.2f %%" % sensor.relative_humidity) return sensor.temperature,sensor.relative_humidity def app_init(): @app.route('/') def index(request): return 'Hello, world!' # 开灯 @app.route('/ledon', methods=['GET']) def ledon(request): print("LED ON") led.value(1) return 'LED ON' # 关灯 @app.route('/ledoff', methods=['GET']) def ledoff(request): print("LED OFF") led.value(0) return 'LED OFF' # 返回一次当前温度和湿度 @app.route('/temp-humidity') def temp_humidity(request): temperature, humidity = get_temp_humidity() return {'temperature': temperature, 'humidity': humidity} # 通过页面更新持续返回当前温度和湿度 @app.route('/temp-humidity2') def temp_humidity(request): from microdot import send_file return send_file('/page/Temperature and Humidity.html') # 聊天室 @app.route('/chat') def send_message(request): from microdot import send_file return send_file('/page/ChatRoom.html') @app.route('/send-message', methods=['POST']) def send_message(request): message = request.json.get('message', '') # 处理消息,例如,在这里你可以调用其他函数来响应不同的命令或消息 print(f'received sessage: {message}') response_message = 'Server received: ' + message return {'message': response_message} # 404页 @app.errorhandler(404) def not_found(request): return {'error': 'resource not found'}, 404 app.run(host=addr, port=5000, debug=False, ssl=None) if __name__ == "__main__": w5x00_init() app_init() ``` /page/ChatRoom.html ``` html Chat Room #chatBox { height: 300px; overflow: auto; background: #f0f0f0; padding: 15px; display: flex; flex-direction: column; } .message { padding: 5px 10px; margin: 5px; border-radius: 5px; max-width: 80%; } .user-message { align-self: flex-end; background-color: #dcf8c6; } .server-message { align-self: flex-start; background-color: #fff; } function sendMessage() { var input = document.getElementById('messageInput'); var message = input.value.trim(); if(message) { displayMessage(message, 'user-message'); // 显示用户消息 input.value = ''; // 清空输入框 fetch('/send-message', { method: 'POST', headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' }, body: JSON.stringify({message: message}) }).then(function(response) { return response.json(); }).then(function(data) { displayMessage(data.message, 'server-message'); // 显示服务端消息 }); } } function displayMessage(text, className) { var chatBox = document.getElementById('chatBox'); var messageElem = document.createElement('div'); messageElem.textContent = text; messageElem.classList.add('message', className); chatBox.appendChild(messageElem); chatBox.scrollTop = chatBox.scrollHeight; // 滚动到最新消息 } Chat Room Follow me 4 by shazhongjin Send ``` /page/Temperature and Humidity.html ``` html Temperature and Humidity function fetchTempHumidity() { fetch('/temp-humidity').then(function(response) { return response.json(); }).then(function(data) { document.getElementById('temperature').textContent = data.temperature; document.getElementById('humidity').textContent = data.humidity; }); } // 每秒执行一次fetchTempHumidity函数 setInterval(fetchTempHumidity, 1000); Temperature: -- Humidity: -- ``` ### 四、演示 [localvideo]eae6acf9bf12349e9820963e59ee1ab2[/localvideo] --- 参考资料: [Installation — Microdot documentation](https://microdot.readthedocs.io/en/v1/intro.html) ## 进阶任务 从NTP服务器(注意数据交互格式的解析)同步时间,获取时间送显示屏(串口)显示。 ### 一、硬件介绍 | 硬件 | 链接、资料 | 图片 | | ----------------------------- | ---- | ---- | | W5500-EVB-Pico | [W5500-EVB-PICO WIZnet 开发板 套 编程器 DigiKey](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/wiznet/W5500-EVB-PICO/16515824) [W5500-EVB-Pico WIZnet Document System](https://docs.wiznet.io/Product/iEthernet/W5500/w5500-evb-pico) |  | | Pico RTC DS3231 | [103030398 Seeed Technology Co., Ltd 开发板 套件 编程器 DigiKey](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/seeed-technology-co-ltd/103030398/14317036) [Pico RTC DS3231 - Waveshare Wiki](https://www.waveshare.com/wiki/Pico-RTC-DS3231) |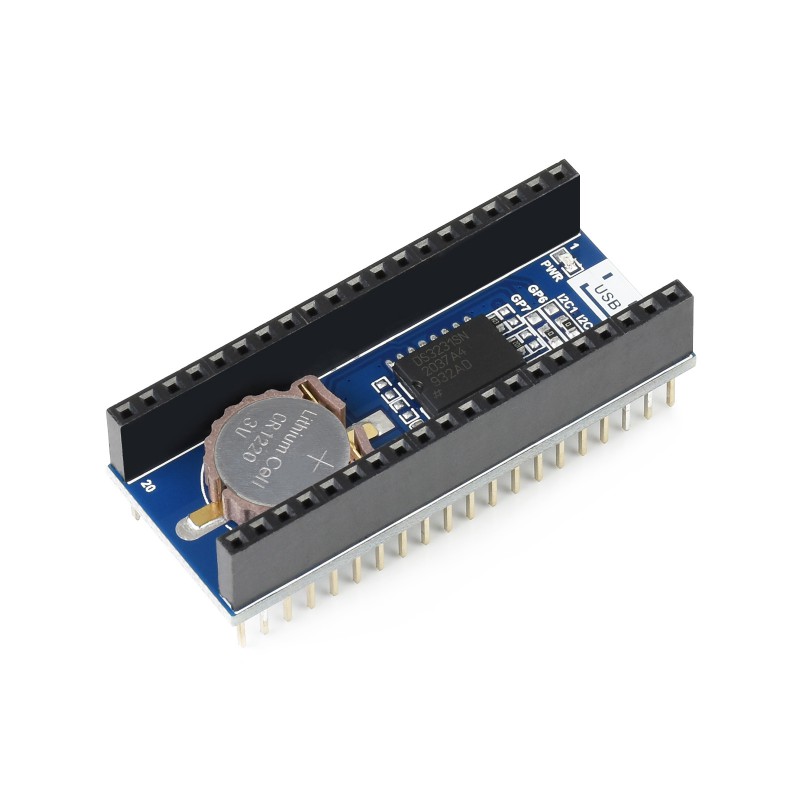  | | Pico LCD 1.14 | [103030400 Seeed Technology Co., Ltd 开发板 套件 编程器 DigiKey](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/seeed-technology-co-ltd/103030400/14317043) [Pico LCD 1.14 - Waveshare Wiki](https://www.waveshare.com/wiki/Pico-LCD-1.14) |  | 接线图1 接线图2 **Pico RTC DS3231** Pico-RTC-DS3231 是专为 Raspberry Pi Pico 设计的 RTC 扩展模块。它集成了高精度RTC芯片DS3231,并使用I2C总线进行通信。由于采用可堆叠设计,可以连接更多的外部传感器。 - 标准树莓派Pico接头,支持树莓派Pico系列。 - 板载高精度RTC芯片DS3231,带备用电池座。 - 实时时钟可计算秒、分、小时、月、月、星期几和年份,闰年补偿有效期至 2100 年。 - 可选格式:24 小时或 12 小时,带 AM/PM 指示器。 - 2 x 可编程闹钟。 - 提供在线文档(Raspberry Pi、Pico、C/C++ 和 MicroPython 示例演示)。 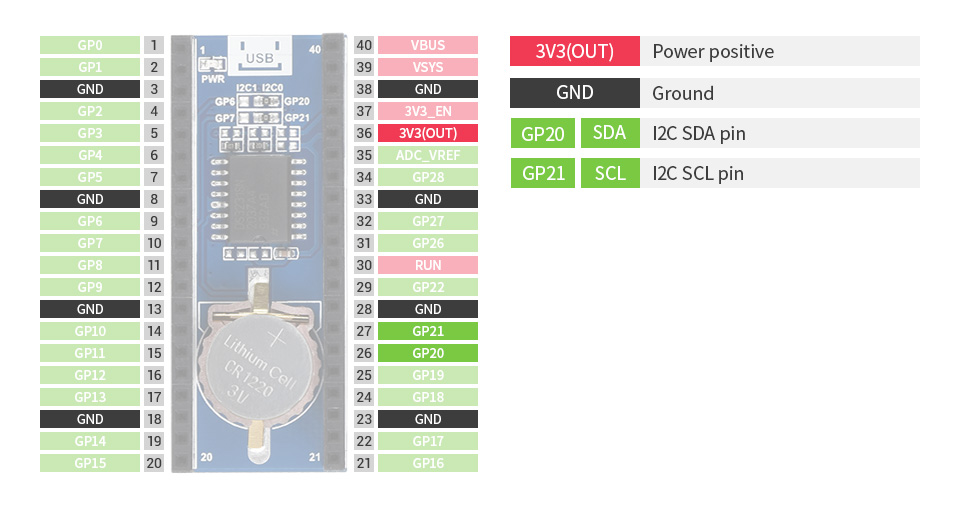 至于为什么会使用DS3231呢?但是主要想搭配这屏幕一起叠高高。一看引脚排列就傻眼了 使用引脚GPIO20、21。GPIO16-21都被w5500使用,所以没办法只能杜邦线来连接DS3231以及屏幕了。 ### 二、驱动RTC ds3231 这里使用了微雪示例代码 ds3231.py ,对ds3231设置时间。 ``` python #!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- from machine import Pin, I2C import time import binascii # the first version use i2c1 #I2C_PORT = 1 #I2C_SDA = 6 #I2C_SCL = 7 # the new version use i2c0,if it dont work,try to uncomment the line 14 and comment line 17 # it should solder the R3 with 0R resistor if want to use alarm function,please refer to the Sch file on waveshare Pico-RTC-DS3231 wiki # https://www.waveshare.net/w/upload/0/08/Pico-RTC-DS3231_Sch.pdf I2C_PORT = 0 I2C_SDA = 20 I2C_SCL = 21 ALARM_PIN = 3 class ds3231(object): # 13:45:00 Mon 24 May 2021 # the register value is the binary-coded decimal (BCD) format # sec min hour week day month year NowTime = b'\x00\x45\x13\x02\x24\x05\x21' w = ["Sunday","Monday","Tuesday","Wednesday","Thursday","Friday","Saturday"]; address = 0x68 start_reg = 0x00 alarm1_reg = 0x07 control_reg = 0x0e status_reg = 0x0f def __init__(self,i2c_port,i2c_scl,i2c_sda): self.bus = I2C(i2c_port,scl=Pin(i2c_scl),sda=Pin(i2c_sda)) def set_time(self,new_time): hour = new_time[0] + new_time[1] minute = new_time[3] + new_time[4] second = new_time[6] + new_time[7] week = "0" + str(self.w.index(new_time.split(",",2)[1])+1) year = new_time.split(",",2)[2][2] + new_time.split(",",2)[2][3] month = new_time.split(",",2)[2][5] + new_time.split(",",2)[2][6] day = new_time.split(",",2)[2][8] + new_time.split(",",2)[2][9] now_time = binascii.unhexlify((second + " " + minute + " " + hour + " " + week + " " + day + " " + month + " " + year).replace(' ','')) #print(binascii.unhexlify((second + " " + minute + " " + hour + " " + week + " " + day + " " + month + " " + year).replace(' ',''))) #print(self.NowTime) self.bus.writeto_mem(int(self.address),int(self.start_reg),now_time) def read_time(self): t = self.bus.readfrom_mem(int(self.address),int(self.start_reg),7) a = t[0]&0x7F #second b = t[1]&0x7F #minute c = t[2]&0x3F #hour d = t[3]&0x07 #week e = t[4]&0x3F #day f = t[5]&0x1F #month print("20%x/%02x/%02x %02x:%02x:%02x %s" %(t[6],t[5],t[4],t[2],t[1],t[0],self.w[t[3]-1])) def set_alarm_time(self,alarm_time): # init the alarm pin self.alarm_pin = Pin(ALARM_PIN,Pin.IN,Pin.PULL_UP) # set alarm irq self.alarm_pin.irq(lambda pin: print("alarm1 time is up"), Pin.IRQ_FALLING) # enable the alarm1 reg self.bus.writeto_mem(int(self.address),int(self.control_reg),b'\x05') # convert to the BCD format hour = alarm_time[0] + alarm_time[1] minute = alarm_time[3] + alarm_time[4] second = alarm_time[6] + alarm_time[7] date = alarm_time.split(",",2)[2][8] + alarm_time.split(",",2)[2][9] now_time = binascii.unhexlify((second + " " + minute + " " + hour + " " + date).replace(' ','')) # write alarm time to alarm1 reg self.bus.writeto_mem(int(self.address),int(self.alarm1_reg),now_time) if __name__ == '__main__': rtc = ds3231(I2C_PORT,I2C_SCL,I2C_SDA) rtc.set_time('13:45:50,Monday,2021-05-24') rtc.read_time() rtc.set_alarm_time('13:45:55,Monday,2021-05-24') ``` ### 三、代码展示 advanced_task_code.py ``` python import network,time,LCD_1inch14,ds3231 from machine import Pin,SPI addr = '' #w5500 初始化 def w5x00_init(): spi=SPI(0,2_000_000, mosi=Pin(19),miso=Pin(16),sck=Pin(18)) nic = network.WIZNET5K() #spi,cs,reset pin # network.WIZNET5K(spi,Pin(17),Pin(20)) nic.active(True) # If you use the Dynamic IP(DHCP), you must use the "nic.ifconfig('dhcp')". nic.ifconfig('dhcp') # If you use the Static IP, you must use the "nic.ifconfig("IP","subnet","Gateway","DNS")". #nic.ifconfig(('192.168.1.108','255.255.255.0','192.168.1.1','8.8.8.8')) while not nic.isconnected(): time.sleep(1) #print(nic.regs()) print(nic.ifconfig()) # Get connection IP global addr addr = nic.ifconfig()[0] def sync_ntp(): import ntptime,machine,time I2C_PORT = 1 I2C_SDA = 26 I2C_SCL = 27 weekday = ["Sunday","Monday","Tuesday","Wednesday","Thursday","Friday","Saturday"]; print("start sync ntp time") # 使用DS3231RTC rtc = ds3231.ds3231(I2C_PORT,I2C_SCL,I2C_SDA) try: ntptime.host = 'ntp1.aliyun.com' # 可选,ntp服务器,默认是"pool.ntp.org" 这里使用阿里服务器 ntptime.settime() # 修改设备时间,到这就已经设置好了 sysrtc = machine.RTC() localtime_now=time.time()+8*3600 localtime_now=time.localtime(localtime_now) sysrtc.datetime((localtime_now[0],localtime_now[1],localtime_now[2],localtime_now[6],localtime_now[3],localtime_now[4],localtime_now[5],localtime_now[7])) year, month, day, weekday, hours, minutes, seconds = sysrtc.datetime()[0:7] # 构造24小时制格式的时间字符串,确保小时、分钟和秒都是两位数 time_str = "{:02d}:{:02d}:{:02d}".format(hours, minutes, seconds) # 构造日期字符串 date_str = "{:04d}-{:02d}-{:02d}".format(year, month, day) # 星期的字典 weekdays = { 0: "Monday", 1: "Tuesday", 2: "Wednesday", 3: "Thursday", 4: "Friday", 5: "Saturday", 6: "Sunday" } # 获取星期几 weekday_str = weekdays.get(weekday, "") # 设置DS3231RTC时间 rtc.set_time(time_str + "," + weekday_str + "," + date_str) print("success sync ntp time") except Exception as e: print("error sync ntp time",repr(e)) if __name__ == "__main__": # 初始化网络 w5x00_init() # 同步ntp时间 sync_ntp() # 初始化LCD LCD = LCD_1inch14.LCD() rtc = ds3231.ds3231(1,27,26) while True: print(f'The SystemRTC time is : {time.localtime()[0]}-{time.localtime()[1]}-{time.localtime()[2]} {time.localtime()[3]}:{time.localtime()[4]}:{time.localtime()[5]} The DS3231RTC time is : {rtc.read_time()[0]}-{rtc.read_time()[1]}-{rtc.read_time()[2]} {rtc.read_time()[3]}:{rtc.read_time()[4]}:{rtc.read_time()[5]} {rtc.read_time()[6]}') LCD.WriteLine(f'The SystemRTC time is : {time.localtime()[0]}-{time.localtime()[1]}-{time.localtime()[2]} {time.localtime()[3]}:{time.localtime()[4]}:{time.localtime()[5]} The DS3231RTC time is : {rtc.read_time()[0]}-{rtc.read_time()[1]}-{rtc.read_time()[2]} {rtc.read_time()[3]}:{rtc.read_time()[4]}:{rtc.read_time()[5]} {rtc.read_time()[6]}') LCD.Clean() ``` /lib/ds3231.py 来自于参考资料连接中微雪例程中文件未做改动,也可本项目提供的源码。 ### 四、演示 [localvideo]915fdcc6a16dc5368d25ef04b69e5388[/localvideo] --- 参考资料: [Pico RTC DS3231 - Waveshare Wiki](https://www.waveshare.com/wiki/Pico-RTC-DS3231) ## 终极任务二 ■ **终极任务二:**使用外部存储器,组建简易FTP文件服务器,并能正常上传下载文件。 ### 一、硬件介绍 本项目中使用到的硬件有: | 硬件 | 链接、资料 | 图片 | | ----------------------------- | ---- | ---- | | W5500-EVB-Pico | [W5500-EVB-PICO WIZnet 开发板 套件 编程器 DigiKey](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/wiznet/W5500-EVB-PICO/16515824) [W5500-EVB-Pico WIZnet Document System](https://docs.wiznet.io/Product/iEthernet/W5500/w5500-evb-pico) |  | | GROVE SHIELD FOR PI PICO V1.0 | [103100142 Seeed Technology Co., Ltd 开发板 套件 编程器 DigiKey](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/seeed-technology-co-ltd/103100142/13688265) |  | | MICROSD CARD BFF QT PY/XIAO | [5683 Adafruit Industries LLC 开发板 套件 编程器 DigiKey](https://www.digikey.cn/zh/products/detail/adafruit-industries-llc/5683/18073185) [Overview Adafruit microSD Card BFF Adafruit Learning System](https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-microsd-card-bff) |  | 接线图1 接线图2 ### 二、设计思路 1. 首先我们需要使用W5500-EVB-Pico连接到网络中。 2. 将sd卡挂载到根目录。 #### 读取SDCard 1. 点击包管理工具,安装sdcard库如下图所示。 2. 使用代码来挂载sd卡。 ``` python import os from sdcard import SDCard from machine import Pin,SPI,SoftSPI spi = SPI(1,2_000_000,sck=Pin(10), mosi=Pin(11), miso=Pin(12)) #spi = SoftSPI(2_000_000,sck=Pin(10), mosi=Pin(11), miso=Pin(12)) # 获取sdcard对象 sd = SDCard(spi, Pin(13)) # 挂载SD卡到/sd目录 os.mount(sd, '/sd') ``` #### 实现FTP文件服务器 造轮子是不可能的这辈子都不可能,既然不造轮子在github上查找下有没有MicroPython FTP库,还真有来自[robert-hh](https://github.com/robert-hh)大神的[FTP-Server-for-ESP8266-ESP32-and-PYBD](https://github.com/robert-hh/FTP-Server-for-ESP8266-ESP32-and-PYBD/tree/master)库。使用库中的uftpd.py文件,该函数使用network.WLAN来获得连接信息。但本项目使用的是w5500控制器来实现网络连接,还需要对start函数稍加小改动。 ``` python # start listening for ftp connections on port 21 def start(port=21, verbose=0, splash=True): global ftpsockets, datasocket global verbose_l global client_list global client_busy alloc_emergency_exception_buf(100) verbose_l = verbose client_list = [] client_busy = False for interface in [network.AP_IF, network.STA_IF]: wlan = network.WLAN(interface) if not wlan.active(): continue ifconfig = wlan.ifconfig() addr = socket.getaddrinfo(ifconfig[0], port) sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) sock.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1) sock.bind(addr[0][4]) sock.listen(1) sock.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, _SO_REGISTER_HANDLER, lambda s : accept_ftp_connect(s, ifconfig[0])) ftpsockets.append(sock) if splash: print("FTP server started on {}:{}".format(ifconfig[0], port)) datasocket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) datasocket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1) datasocket.bind(('0.0.0.0', _DATA_PORT)) datasocket.listen(1) datasocket.settimeout(10) def restart(port=21, verbose=0, splash=True): stop() sleep_ms(200) start(port, verbose, splash) ``` 改动思路: 1. 在uftpd.py 的 start函数中,将WLAN改为WIZNET5K,从WIZNET5K对象中获得网络连接信息。 ``` python # start listening for ftp connections on port 21 def start(port=21, verbose=0, splash=True): global ftpsockets, datasocket global verbose_l global client_list global client_busy alloc_emergency_exception_buf(100) verbose_l = verbose client_list = [] client_busy = False nic = network.WIZNET5K() if not nic.active(): continue ifconfig = nic.ifconfig() addr = socket.getaddrinfo(ifconfig[0], port) sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) sock.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1) sock.bind(addr[0][4]) sock.listen(1) sock.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, _SO_REGISTER_HANDLER, lambda s : accept_ftp_connect(s, ifconfig[0])) ftpsockets.append(sock) if splash: print("FTP server started on {}:{}".format(ifconfig[0], port)) datasocket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) datasocket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1) datasocket.bind(('0.0.0.0', _DATA_PORT)) datasocket.listen(1) datasocket.settimeout(10) def restart(port=21, verbose=0, splash=True): stop() sleep_ms(200) start(port, verbose, splash) ``` 修改后在执行过程中一直无法成功创建FTP服务,经过分析找到了问题的原因。当在uftpd.py文件中再此执行 `network.WIZNET5K()` 时似乎他创建了一个新的nic对象,而不是使用 `network.WLAN()` 时返回的是当前的网络连接对象。所以在判断 `not nic.active()` 结果永远为True。程序无法继续运行下去。 2. 不妨换个思路在uftpd.start函数中获得网络对象的目的为获得当前网络连接分配的IP地址。干脆让start函数传入ip参数。这样程序就能顺利执行。也不会卡在`network.WIZNET5K()`这个问题上了。 ``` python # start listening for ftp connections on port 21 def start(host='0.0.0.0',port=21, verbose=0, splash=True): global ftpsockets, datasocket global verbose_l global client_list global client_busy alloc_emergency_exception_buf(100) verbose_l = verbose client_list = [] client_busy = False addr = socket.getaddrinfo(host, port) sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) sock.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1) sock.bind(addr[0][4]) sock.listen(1) sock.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, _SO_REGISTER_HANDLER, lambda s : accept_ftp_connect(s,host)) ftpsockets.append(sock) if splash: print("FTP server started on {}:{}".format(host, port)) datasocket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) datasocket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1) datasocket.bind(('0.0.0.0', _DATA_PORT)) datasocket.listen(1) datasocket.settimeout(10) def restart(host='0.0.0.0',port=21, verbose=0, splash=True): stop() sleep_ms(200) start(port, verbose, splash) ``` ### 三、代码展示 /ultimate_task2_code.py ``` python import network,time from machine import Pin,SPI addr = '' #w5500 初始化 def w5x00_init(): spi=SPI(0,2_000_000, mosi=Pin(19),miso=Pin(16),sck=Pin(18)) nic = network.WIZNET5K(spi,Pin(17),Pin(20)) #spi,cs,reset pin # network.WIZNET5K(spi,Pin(17),Pin(20)) nic.active(True) # If you use the Dynamic IP(DHCP), you must use the "nic.ifconfig('dhcp')". nic.ifconfig('dhcp') # If you use the Static IP, you must use the "nic.ifconfig("IP","subnet","Gateway","DNS")". #nic.ifconfig(('192.168.2.107','255.255.255.0','192.168.2.1','8.8.8.8')) while not nic.isconnected(): time.sleep(1) #print(nic.regs()) print(nic.ifconfig()) # Get connection IP global addr addr = nic.ifconfig()[0] def sdcard_init(path='/sd'): import os from sdcard import SDCard from machine import Pin,SPI,SoftSPI spi = SPI(1,2_000_000,sck=Pin(10), mosi=Pin(11), miso=Pin(12)) #spi = SoftSPI(2_000_000,sck=Pin(10), mosi=Pin(11), miso=Pin(12)) # 获取sdcard对象 sd = SDCard(spi, Pin(13)) # 挂载SD卡到/sd目录 os.mount(sd, path) print(f'success mounted sdcard in \'{path}\'') if __name__ == "__main__": # 初始化网络 w5x00_init() # 初始化并挂在sd卡 sdcard_init() import uftpd uftpd.start(host = addr,port = 21,verbose = 0) ``` /lib/uftp.py ``` python # # Small ftp server for ESP8266 Micropython # Based on the work of chrisgp - Christopher Popp and pfalcon - Paul Sokolovsky # # The server accepts passive mode only. It runs in background. # Start the server with: # # import uftpd # uftpd.start([port = 21][, verbose = level]) # # port is the port number (default 21) # verbose controls the level of printed activity messages, values 0, 1, 2 # # Copyright (c) 2016 Christopher Popp (initial ftp server framework) # Copyright (c) 2016 Paul Sokolovsky (background execution control structure) # Copyright (c) 2016 Robert Hammelrath (putting the pieces together and a # few extensions) # Copyright (c) 2020 Jan Wieck Use separate FTP servers per socket for STA + AP mode # Copyright (c) 2021 JD Smith Use a preallocated buffer and improve error handling. # Distributed under MIT License # import socket import network import uos import gc import sys import errno from time import sleep_ms, localtime from micropython import alloc_emergency_exception_buf # constant definitions _CHUNK_SIZE = const(1024) _SO_REGISTER_HANDLER = const(20) _COMMAND_TIMEOUT = const(300) _DATA_TIMEOUT = const(100) _DATA_PORT = const(13333) # Global variables ftpsockets = [] datasocket = None client_list = [] verbose_l = 0 client_busy = False # Interfaces: (IP-Address (string), IP-Address (integer), Netmask (integer)) _month_name = ("", "Jan", "Feb", "Mar", "Apr", "May", "Jun", "Jul", "Aug", "Sep", "Oct", "Nov", "Dec") class FTP_client: def __init__(self, ftpsocket, local_addr): self.command_client, self.remote_addr = ftpsocket.accept() self.remote_addr = self.remote_addr[0] self.command_client.settimeout(_COMMAND_TIMEOUT) log_msg(1, "FTP Command connection from:", self.remote_addr) self.command_client.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, _SO_REGISTER_HANDLER, self.exec_ftp_command) self.command_client.sendall("220 Hello, this is the {}.\r\n".format(sys.platform)) self.cwd = '/' self.fromname = None # self.logged_in = False self.act_data_addr = self.remote_addr self.DATA_PORT = 20 self.active = True self.pasv_data_addr = local_addr def send_list_data(self, path, data_client, full): try: for fname in uos.listdir(path): data_client.sendall(self.make_description(path, fname, full)) except Exception as e: # path may be a file name or pattern path, pattern = self.split_path(path) try: for fname in uos.listdir(path): if self.fncmp(fname, pattern): data_client.sendall( self.make_description(path, fname, full)) except: pass def make_description(self, path, fname, full): global _month_name if full: stat = uos.stat(self.get_absolute_path(path, fname)) file_permissions = ("drwxr-xr-x" if (stat[0] & 0o170000 == 0o040000) else "-rw-r--r--") file_size = stat[6] tm = stat[7] & 0xffffffff tm = localtime(tm if tm < 0x80000000 else tm - 0x100000000) if tm[0] != localtime()[0]: description = "{} 1 owner group {:>10} {} {:2} {:>5} {}\r\n".\ format(file_permissions, file_size, _month_name[tm[1]], tm[2], tm[0], fname) else: description = "{} 1 owner group {:>10} {} {:2} {:02}:{:02} {}\r\n".\ format(file_permissions, file_size, _month_name[tm[1]], tm[2], tm[3], tm[4], fname) else: description = fname + "\r\n" return description def send_file_data(self, path, data_client): buffer = bytearray(_CHUNK_SIZE) mv = memoryview(buffer) with open(path, "rb") as file: bytes_read = file.readinto(buffer) while bytes_read > 0: data_client.write(mv[0:bytes_read]) bytes_read = file.readinto(buffer) data_client.close() def save_file_data(self, path, data_client, mode): buffer = bytearray(_CHUNK_SIZE) mv = memoryview(buffer) with open(path, mode) as file: bytes_read = data_client.readinto(buffer) while bytes_read > 0: file.write(mv[0:bytes_read]) bytes_read = data_client.readinto(buffer) data_client.close() def get_absolute_path(self, cwd, payload): # Just a few special cases "..", "." and "" # If payload start's with /, set cwd to / # and consider the remainder a relative path if payload.startswith('/'): cwd = "/" for token in payload.split("/"): if token == '..': cwd = self.split_path(cwd)[0] elif token != '.' and token != '': if cwd == '/': cwd += token else: cwd = cwd + '/' + token return cwd def split_path(self, path): # instead of path.rpartition('/') tail = path.split('/')[-1] head = path[:-(len(tail) + 1)] return ('/' if head == '' else head, tail) # compare fname against pattern. Pattern may contain # the wildcards ? and *. def fncmp(self, fname, pattern): pi = 0 si = 0 while pi < len(pattern) and si < len(fname): if (fname[si] == pattern[pi]) or (pattern[pi] == '?'): si += 1 pi += 1 else: if pattern[pi] == '*': # recurse if pi == len(pattern.rstrip("*?")): # only wildcards left return True while si < len(fname): if self.fncmp(fname[si:], pattern[pi + 1:]): return True else: si += 1 return False else: return False if pi == len(pattern.rstrip("*")) and si == len(fname): return True else: return False def open_dataclient(self): if self.active: # active mode data_client = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) data_client.settimeout(_DATA_TIMEOUT) data_client.connect((self.act_data_addr, self.DATA_PORT)) log_msg(1, "FTP Data connection with:", self.act_data_addr) else: # passive mode data_client, data_addr = datasocket.accept() log_msg(1, "FTP Data connection with:", data_addr[0]) return data_client def exec_ftp_command(self, cl): global datasocket global client_busy global my_ip_addr try: gc.collect() try: data = cl.readline().decode("utf-8").rstrip("\r\n") except OSError: # treat an error as QUIT situation. data = "" if len(data) > 8, _DATA_PORT % 256)) self.active = False elif command == "PORT": items = payload.split(",") if len(items) >= 6: self.act_data_addr = '.'.join(items[:4]) if self.act_data_addr == "127.0.1.1": # replace by command session addr self.act_data_addr = self.remote_addr self.DATA_PORT = int(items[4]) * 256 + int(items[5]) cl.sendall('200 OK\r\n') self.active = True else: cl.sendall('504 Fail\r\n') elif command == "LIST" or command == "NLST": if payload.startswith("-"): option = payload.split()[0].lower() path = self.get_absolute_path( self.cwd, payload[len(option):].lstrip()) else: option = "" try: data_client = self.open_dataclient() cl.sendall("150 Directory listing:\r\n") self.send_list_data(path, data_client, command == "LIST" or 'l' in option) cl.sendall("226 Done.\r\n") data_client.close() except: cl.sendall('550 Fail\r\n') if data_client is not None: data_client.close() elif command == "RETR": try: data_client = self.open_dataclient() cl.sendall("150 Opened data connection.\r\n") self.send_file_data(path, data_client) # if the next statement is reached, # the data_client was closed. data_client = None cl.sendall("226 Done.\r\n") except: cl.sendall('550 Fail\r\n') if data_client is not None: data_client.close() elif command == "STOR" or command == "APPE": try: data_client = self.open_dataclient() cl.sendall("150 Opened data connection.\r\n") self.save_file_data(path, data_client, "wb" if command == "STOR" else "ab") # if the next statement is reached, # the data_client was closed. data_client = None cl.sendall("226 Done.\r\n") except: cl.sendall('550 Fail\r\n') if data_client is not None: data_client.close() elif command == "SIZE": try: cl.sendall('213 {}\r\n'.format(uos.stat(path)[6])) except: cl.sendall('550 Fail\r\n') elif command == "MDTM": try: tm=localtime(uos.stat(path)[8]) cl.sendall('213 {:04d}{:02d}{:02d}{:02d}{:02d}{:02d}\r\n'.format(*tm[0:6])) except: cl.sendall('550 Fail\r\n') elif command == "STAT": if payload == "": cl.sendall("211-Connected to ({})\r\n" " Data address ({})\r\n" " TYPE: Binary STRU: File MODE: Stream\r\n" " Session timeout {}\r\n" "211 Client count is {}\r\n".format( self.remote_addr, self.pasv_data_addr, _COMMAND_TIMEOUT, len(client_list))) else: cl.sendall("213-Directory listing:\r\n") self.send_list_data(path, cl, True) cl.sendall("213 Done.\r\n") elif command == "DELE": try: uos.remove(path) cl.sendall('250 OK\r\n') except: cl.sendall('550 Fail\r\n') elif command == "RNFR": try: # just test if the name exists, exception if not uos.stat(path) self.fromname = path cl.sendall("350 Rename from\r\n") except: cl.sendall('550 Fail\r\n') elif command == "RNTO": try: uos.rename(self.fromname, path) cl.sendall('250 OK\r\n') except: cl.sendall('550 Fail\r\n') self.fromname = None elif command == "CDUP" or command == "XCUP": self.cwd = self.get_absolute_path(self.cwd, "..") cl.sendall('250 OK\r\n') elif command == "RMD" or command == "XRMD": try: uos.rmdir(path) cl.sendall('250 OK\r\n') except: cl.sendall('550 Fail\r\n') elif command == "MKD" or command == "XMKD": try: uos.mkdir(path) cl.sendall('250 OK\r\n') except: cl.sendall('550 Fail\r\n') elif command == "SITE": try: exec(payload.replace('\0','\n')) cl.sendall('250 OK\r\n') except: cl.sendall('550 Fail\r\n') else: cl.sendall("502 Unsupported command.\r\n") # log_msg(2, # "Unsupported command {} with payload {}".format(command, # payload)) except OSError as err: if verbose_l > 0: log_msg(1, "Exception in exec_ftp_command:") sys.print_exception(err) if err.errno in (errno.ECONNABORTED, errno.ENOTCONN): close_client(cl) # handle unexpected errors except Exception as err: log_msg(1, "Exception in exec_ftp_command: {}".format(err)) # tidy up before leaving client_busy = False def log_msg(level, *args): global verbose_l if verbose_l >= level: print(*args) # close client and remove it from the list def close_client(cl): cl.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, _SO_REGISTER_HANDLER, None) cl.close() for i, client in enumerate(client_list): if client.command_client == cl: del client_list break def accept_ftp_connect(ftpsocket, local_addr): # Accept new calls for the server try: client_list.append(FTP_client(ftpsocket, local_addr)) except: log_msg(1, "Attempt to connect failed") # try at least to reject try: temp_client, temp_addr = ftpsocket.accept() temp_client.close() except: pass def num_ip(ip): items = ip.split(".") return (int(items[0])
- 2024-02-14
-
上传了资料: 【得捷电子Follow me第4期 任务成果代码
- 2024-02-11
-
加入了学习《直播回放: FollowMe 4 W5500-EVB-Pico 使用入门》,观看 W5500-EVB-Pico 使用入门
- 2024-01-17
-
加入了学习《利用机器视觉打造带有全自动老板键的智能键盘》,观看 利用机器视觉打造带有全自动老板键的智能键盘
回复过的帖子
统计信息
已有8人来访过
- 芯积分:102
- 好友:--
- 主题:4
- 回复:4
留言

现在还没有留言
推荐博文
- 基于晶尊微SC09B触摸芯片实现的ICMAN触摸滑条调光
- 如何应对ADAS/AD海量数据处理挑战?
- EMC测试基本环境要求 - GM GMW3097 2012
- 嵌入式开发必备-RK3562演示Linux常用系统查询命令(上)深圳触觉智能出品
- 开源鸿蒙OpenHarmony系统更换开机Logo方法,瑞芯微RK3566鸿蒙开发板
- DDR4的单、双DIE兼容,不做仿真行不行?
- 【B-G431B-ESC1-电机开发板试用】-02-串口,定时器-LED灯的测试
- XD08M3232接近感应单片机的开发难点
- 12G-SDI高清视频开发案例,让4K视频采集更便捷!基于Xilinx MPSoC高性能平台
- 触觉智能Purple Pi OH鸿蒙开发板成功适配OpenHarmony5.0 Release,开启新征程
- 嵌入式工程师AI挑战营RV1106人脸识别+板卡烧录系统(0)
- Vision板子和机器视觉omv
- 【Follow me第二季第3期】基础任务:quad-spi flash和octo-spi flash读写速度测试
- 一起读《动手学深度学习(PyTorch版)》- 权重衰减(weight decay)
- 无源晶振有方向吗